Cartilage is called connective tissue, which is present in many parts of the body. Although cartilage is stiff and flexible, damaging it is fairly easy.
Cartilage plays an important role in the human body:
- reduces friction and acts as a pillow between joints;
- helps maintain weight when we run, bend, or stretch a limb
- holds bones together, for example, chest bones;
- some parts of the body are almost entirely cartilage, for example, the outer parts of the ears;
- in children, the ends of long bones are made of cartilage, which ultimately turns into bone.
Unlike other types of tissue, cartilage does not have blood supply. Because of this, restoration of the cartilage tissue of the joints takes a lot of time, compared to other tissues that are supplied with blood.
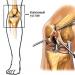
Figure 1 Micro-destructive or stimulating bone marrow therapy: with a minimally invasive procedure, small holes are drilled into cartilage damage to establish a connection with the bone marrow. From this, stem cells flow into a cartilage defect, where they create a new cartilage layer, becoming cartilage cells.
Figure 2: Cartilage transplantation: Cartilage cells are removed from healthy cartilage tissue by puncture in order to propagate them in the laboratory. Cartilage cells grown in this way are introduced into an open procedure at the defective site of the cartilage, where they build new cartilage tissue.
There are three types of cartilage:
- Elastic cartilage (yellow cartilage)- the most resilient and elastic type of cartilage. Elastic cartilage makes up the outside of the ears, and part of the nose.
- Bone - the toughest type of cartilage that can withstand heavy weight. It is located between the discs and vertebrae of the spine and between the bones of the thigh and pelvis.
- Hyaline cartilage - elastic and hard. Such cartilage is located between the ribs, around the trachea, as well as between the joints (articular cartilage).
All three types of cartilage can be damaged. When the cartilage in the joint is damaged, it can cause severe pain, inflammation, and even lead to disability. According to statistics from the U.S. National Institute of Health, one third of adult Americans over the age of 45 suffer from knee pain caused by damage to cartilage.
How does patellar cartilage disease progress?
How can cartilage damage be prevented? The most important thing is the movement. Ideal sports such as cycling, swimming and quite a push, because the knee is not twisted, and the tension on the joint is low. Pure training leads to sports that are more stable and therefore less prone to cartilage injuries.
How does cartilage regenerative therapy work? For each type of tissue regeneration, you need cells that rebuild the tissue, in this case the cartilage layer, on the damaged area. For this, we currently use mainly two methods of therapy. First, we use stem cells from bone marrow. Stem cells are cells that can create many different tissues. They are part of the body's natural repair mechanism. So we are using something here that the body does on its own, but not at this point in the body.
The causes of destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joint
- Direct hit - if the joint is exposed to excessive impact, for example, during intense training, a failed fall, or a car accident. Athletes have a higher risk of joint damage, especially if they engage in sports with increased joint stress, such as American football, rugby, and wrestling.
- Wear - A joint that experiences a long period of stress can be damaged. Obese people are more likely to suffer from knee cartilage wear than a normal-weight person, simply because their body is under a much higher degree of physical activity.
- Prolonged inflammation, and ultimately the loss of cartilage in the joints. This condition is known as osteoarthritis.
- Lack of movement - The joints should move regularly to stay healthy. Long periods of downtime or immobility increase the risk of cartilage damage.
If measures are not taken to restore the cartilage tissue of the joints, this can lead to such severe damage that a person cannot walk. In addition to immobility, patients are worried about severe pain. All minor defects in the articular cartilage can ultimately lead to osteoarthritis if enough time passes.
For this purpose, we drill small holes in the damage to the cartilage and thereby establish a connection between the internal joint and the bone marrow. Through these openings, stem cells from the bone marrow penetrate into a cartilage defect. There they create a new layer of cartilage, becoming cartilage cells. In technical jargon, such treatment methods are called bone marrow stimulation methods.
Why can cartilage tissue break down?
And what is the second therapy? In the second method, new cartilage cells are grown outside the body. To do this, remove a piece of healthy cartilage from the patient, disconnect the cells and propagate them in the laboratory. Cells thus grown then return to the defective site of the cartilage, where they begin to build new cartilage tissue.
General principles
 There are a number of non-surgical treatments that can help relieve symptoms of damage to articular cartilage.
There are a number of non-surgical treatments that can help relieve symptoms of damage to articular cartilage.
Physiotherapy - Exercises that strengthen the muscles surrounding or supporting the joint can help reduce pressure on the joint and reduce pain.
How to decide which of the two therapies will be used? Cartilage transplantation is particularly suitable for serious cartilage damage. It is often used in younger patients after a serious knee injury, but with other joints intact. However, bone marrow stimulation procedures are likely to be used for minor damage. Basically, they can be minimally invasive, which means that surgical instruments reach the joint through the smallest incisions.
In contrast, cartilage transplantation occurs on the open knee, which is a little more stressful for the patient. What determines the success of therapy? Crucial to success is that the knee is not damaged except for damage to the cartilage. If not, concomitant injuries such as cruciate ligaments or patella, as well as adverse abnormalities, such as misalignment of the axis of the leg, should be treated before the treatment of cartilage. Because these are all factors that have a negative effect on the damaged area of \u200b\u200bcartilage.
Painkillers Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen, help reduce swelling and pain.
Chondroprotective agentsthat prevent further destruction of cartilage.
Supporting devices - such as a cane.
Lifestyle changes - such as a decrease in activity that involves the affected joint.
Cartilage structure
In other words, you must always solve the cartilage problem holistically. This is the most important requirement for all cartilage techniques. This requires a deep understanding of how the knee works, based on the complex interaction of biomechanical principles and biological processes.
How long is mobility limited after surgery? After both procedures, rehabilitation is similar. In the first six weeks after surgery, patients can only partially load the knee and are forced to walk on crutches. In addition, they get an electric motion tire that bends and stretches the knee. After six weeks, they can walk normally and begin to restore lost muscle mass.
In more severe cases, when restoration of the cartilaginous tissue of the joints is impossible and the joint has lost mobility, the doctor may recommend surgical intervention. Surgical treatment of damaged articular cartilage includes the following procedures: arthroscopic debridement, bone marrow stimulation, bone transplantation, implantation of autologous chondrocytes. Innovative methods of cartilage restoration include growing new cartilage from the stem cells of the patient himself, but he is still undergoing research.
How to restore cartilage with therapy
Walking fast, catch a bus, carry a shopping bag up the stairs or tie your shoelaces with squats - with healthy joints, no problem. But those who suffer from joint pain are often severely limited in their lives and can no longer perform many actions, as usual. Today, several million people in Germany suffer from joint pain. Especially often in people over the age of arthritis. Here, 50% of women suffer, in men this is a good third.
What causes joint pain?
There are many joint diseases - the most common of which is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis develops slowly and affects not only the elderly. Excessive or incorrect load on the joint, permanent improper location, for example. For example, joint sports, obesity, physical inactivity, unrest, severe trauma in the past, joint surgery, genetic predisposition. Osteoarthritis is especially dependent on weight knee joint and hip joints.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, abbreviated NSAIDs, are used to reduce pain, heat, swelling and redness of the skin associated with a disease (or trauma) that caused cartilage damage. The three most commonly used NSAIDs are aspirin, paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Aspirin is one of the most misused drugs because of its wide availability. It has several mechanisms of action.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
The disease begins with a slow but ongoing degeneration of the articular cartilage. If untreated, arthritic artery disease leads to a damaged or destroyed joint surface, where the bones rub the bones, causing severe pain. The first signs of osteoarthritis are usually non-specific. Initially, the pain is especially noticeable in the case of impulse loads, with increased wear, even the movement flows painlessly, back pain and night pain can be added later.
Treatment for osteoarthritis?
If the joints often redden or overheat, it may be due to abrasive cartilage or bone, which causes inflammation. Conventional medicine does not know the causative treatment of arthrosis, as once removed cartilage cannot grow. An old, healthy state of the joint cannot be restored, but there are ways and means to reduce the state of pain to an acceptable level - whether it be physiotherapy or analgesic therapy, physiotherapy, drug therapy, orthopedic technology or even surgical measures.
- Firstly, it prevents pain signals from entering the part of the brain called the thalamus.
- Aspirin also irreversibly inhibits chemical inflammatory mediators that cause pain and additional inflammatory reactions.
- In addition, aspirin reduces fever, has an effect on the hypothalamus in the brain, which leads to vasodilation and sweating.
Side effects of aspirin include indigestion, heartburn, nausea, tinnitus (tinnitus), headache, and diarrhea. Aspirin has an effect on the blood coagulation system, which means that bleeding in damaged tissue can be intensified. It can also increase soft tissue swelling and, therefore, increase the period required for rehabilitation after an injury.
Therefore, the goal of therapy should be to ensure joint mobility, prevent the progression of osteoarthritis and alleviate the resulting pain. Monitor daily wear over time. Exercise regularly and, above all, choose joint sports. Swimming, cycling, walking and cross-country skiing are ideal. With proper gymnastics, you can also strengthen and build up joints that are usually affected by osteoarthritis. These include large jointssuch as hips and knees.
Proper nutrition can also help prevent inflammation and, thus, help reduce the level of pain, because with the right lifestyle you can slow down the course of the disease. Also, prepared meals, too much caffeine, alcohol and sugar should be largely eliminated from your diet or at least reduced to a small degree. If you have been diagnosed with osteoarthritis, you can learn to live happier with proper nutrition, physical therapy, and regular exercise.
Despite the fact that ibuprofen also has analgesic (analgesic) and antipyretic effects, it does not affect blood coagulation to the same extent as aspirin.
Paracetamol It does not have significant anti-inflammatory effects, but it has an antipyretic and analgesic effect. It is effective in relieving moderate pain and does not affect the stomach.
Mandatory activity in the damaged area!
Most injuries and sports accidents are responsible for damage to the cartilage of the ankle. Unlike wear and age-related forms of osteoarthritis, these cartilage injuries, which are medically related to osteochondral injuries, occur in athletes under the age of 40 years. Patients often report long suffering in a doctor’s conversation: Diffuse discomfort on the upper ankle, sports restrictions, ankle swelling after activity, and loss of strength are signs of cartilage injuries.
Due to possible side effects, all NSAIDs should be prescribed only by a doctor.
Chondroprotective Agents - non-hormonal drugs used to treat degenerative processes in arthritis and contribute to the normalization of synovial fluid and cartilage matrix. They stimulate the synthesis of chondrocytes of collagen and proteoglycans, as well as the production of hyaluronic acid, inhibit the degradation of cartilage; and prevents the formation of fibrin in the subchondral and synovial vasculature.
The specialist should also look at the external ligaments and the stability of the axis of the foot: disturbances and unstable external ligaments can lead to long-term injuries of the cartilage. In addition to sports injuries, bone death, often with an unknown cause, can weaken the overlying cartilage in the ankle.
How can cartilage graft save a joint?
The sooner the patient receives special treatment after the onset of symptoms, the better his or her prospects for restoring or maintaining athletic abilities. Inoculation of cartilage in the ankle can restore the smooth surface of the cartilage. Processes such as osteoarthritis and articular clothing can be stopped for the first time and vice versa. The long-term effectiveness of cartilage transplantation for the treatment of cartilage defects is also confirmed by several years of evaluation of cartilage transplantation.
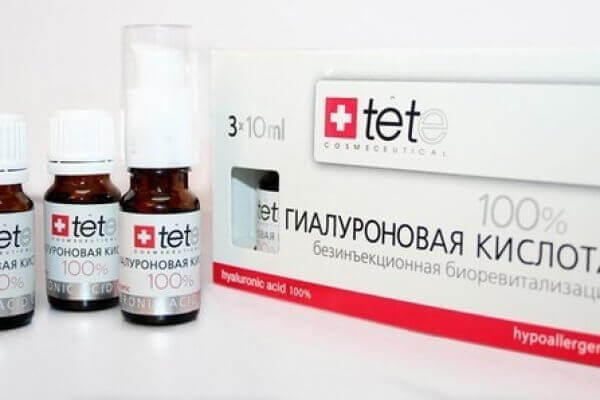 The following chondroprotective drugs are usually prescribed to restore the cartilage of the joints:
The following chondroprotective drugs are usually prescribed to restore the cartilage of the joints:
It serves as a lubricant and shock absorber in the synovial fluid, and is located in the vitreous body of the eye. HA is not well absorbed by oral use, but is widely used in the form of injections in a sore joint.
Nutritional changes
Autologous cartilage cells are transplanted during cartilage transplantation. Therefore, they speak of autologous cartilage transplantation. In this case, the body’s own cartilage cells are obtained in a small procedure as microscopic particles, as far as possible, from the unloaded area of \u200b\u200bthe affected joint. These cartilage cells are grown in the laboratory and multiplied more than a thousand times. Such quick cartilage regeneration would be impossible in the body. Since the body’s own cells are used for transplantation, it comes to good growth.
Possible mechanisms by which HA can act therapeutically include:
- providing additional lubrication of the synovial membrane;
- control of the permeability of the synovial membrane, thereby controlling the effusion;
- direct blocking of inflammation by getting rid of free radicals.
Glucosamine. Numerous in vitro studies have shown that glucosamine stimulates the synthesis of proteoglycans and collagen by chondrocytes. Glucosamine also has a mild anti-inflammatory effect. The effects of glucosamine therapy have been studied using the intravenous, intramuscular, and oral routes. When administered orally, about 87% of the administered dose is absorbed by the body. The use of glucosamine for the treatment of osteoarthritis is convenient and well tolerated by patients.
Cartilage Transplantation Steps
Incompatibility or deviation does not occur. After 6 weeks, the new cartilage stabilized so that a partial load on the ankle could begin. After the procedure, a three-day hospital stay is required. After 6 weeks, a partial load is possible after 3 months of full joint loading. The long-term success of the process is good.
Who can help cartilage transplantation in the ankle?
Cartilage biological regeneration methods have been in medical use for 15 years. 
Cartilage cell transplantation is valuable as a measure to preserve the joint, especially in younger patients under the age of 40 years. The requirements for athletic resilience and ankle flexibility are especially strong here. Cartilage transplantation is particularly suitable for maintaining ankle's athletic ability. For minor injuries, other procedures may be used. Only after having worked out all the orthopedic reasons can a specialist provide a good prognosis of ankle's athletic ability after cartilage transplantation.
Chondroitin Sulfate. This substance is a natural component in several tissues in the body in addition to cartilage, including those found in the tendons, bones, cornea, and heart valve.
 As a chondroprotective agent of chondroitin, sulfate has a metabolic effect and also competitively inhibits many cartilage-destroying enzymes. Also, according to the latest research, the intake of chondroitin sulfate can prevent the formation of fibrin thrombi in synovial or subchondral microvessels. Chondroitin also has an anti-atherosclerotic effect.
As a chondroprotective agent of chondroitin, sulfate has a metabolic effect and also competitively inhibits many cartilage-destroying enzymes. Also, according to the latest research, the intake of chondroitin sulfate can prevent the formation of fibrin thrombi in synovial or subchondral microvessels. Chondroitin also has an anti-atherosclerotic effect.
Theoretically, taking this drug orally and as an ointment or cream increases blood flow to the tissues. Although this is a large molecule, the bioavailability of chondroitin after oral administration has been well documented. The human body and experimental animals absorbed about 70% of the orally administered chondroitin sulfate.
Physiotherapy
A sedentary lifestyle reduces the amount of proteoglycans (protective molecules) in the cartilage and leads to rapid wear of the cartilage. Therefore, physiotherapy exercises are successfully used to restore the cartilage tissue of joints in overweight patients or leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Thanks to exercise therapy exercises, such as a bicycle, blood flow to the diseased area improves, ligaments become stronger and the focus of inflammation decreases. It is also very useful swimming, it significantly reduces the load on the joints.
How to restore joints with diet and folk remedies
 Glycine and proline are the most common amino acids in the collagen fibers of human tissues. Although the body can produce these proteins, a low-protein diet can create glycine and proline deficiency.
Glycine and proline are the most common amino acids in the collagen fibers of human tissues. Although the body can produce these proteins, a low-protein diet can create glycine and proline deficiency.
But these substances are abundant in gelatin. Therefore, patients with arthritis and arthrosis, as well as those who are looking for how to restore joints using natural methods, are recommended to include bone-broth rich in gelatin in their diet.
Refined carbohydrates should be avoided in foods such as white flour foods, white rice, and sugary foods and drinks.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a great example of how to repair joints without the help of drugs. However, physiotherapy works best in combination with drug therapy.
- thermal procedures;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- electropulse muscle stimulation;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Usually they are carried out in a clinic or hospital, after which the patient can return home.
Folk remedies
Ginger is a popular home remedy for treating knee pain caused by cartilage wear. Its effectiveness is due to the presence of anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Grind a small piece of fresh ginger, add one glass of water and cook for 10 minutes.
- Strain and add a little honey and lemon juice to the broth.
- Drink two to three cups of this ginger infusion daily until the pain disappears.
- You can also massage your sore knee with ginger oil two or three times a day.
Recover synovial fluid
Olive oil is a good source of lubricin. It is a protein that improves the ability of synovial fluid to protect surrounding cartilage and serves as a lubricant.
A regular dose of olive oil helps regenerate synovial fluid. Since drinking olive oil every day will be difficult even for the sake of maintaining healthy joints, it is enough to use olive oil to season a salad or a meal.
Huge bules, all the regular and casual guests of this blog! Once again, we will talk about the terrible danger that lies in wait for our cartilage. These valiant workaholic literally smooth out all the jagged corners in our body and help us move smoothly and smoothly. Without them, we would simply resemble old ruins and could not take a step.
Few people know how to restore the cartilage of the spine. Today we will understand which methods work and which are completely meaningless.
Already in 30-year-old patients, doctors diagnose cartilage tissue surface dislocation. If you place such samples under a microscope, you can see small microcracks on them.
 After 40 years, ubiquitous cartilage aging begins. The main problem is that this protective tissue is rapidly losing one of its main components - water (it is here about 75%).
After 40 years, ubiquitous cartilage aging begins. The main problem is that this protective tissue is rapidly losing one of its main components - water (it is here about 75%).
And we don’t really need to talk about the role of water in our body: everyone already understands its extreme importance.
The less water in the cartilage, the less its strength. The second problem is the low metabolic activity of this structure.
For comparison, the protein component of the liver completely regenerates after 4 days, but the cartilage is in no hurry. Its collagen cells will change their composition by half only after 10 years.
Now, my prudent reader, do you understand why even the most minor damage to cartilage in the spine is so dangerous ?! Let’s figure out what the mysterious fabric is in front of us.
What does cartilage consist of and what complicates its life?
This type of fabric is connective and performs supporting functions. Each cartilage also has a so-called perichondrium (except articular, where synovial fluid plays this role). Thanks to her, the tissue grows and receives nutrition.
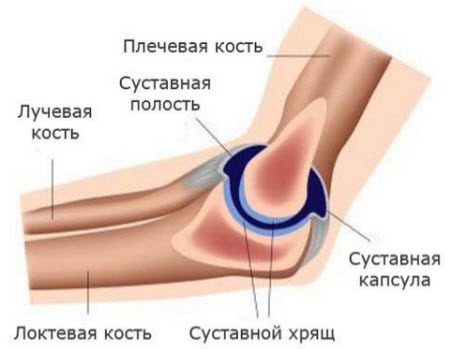
Cartilage life is not easy: they constantly feel static and dynamic loads. Their structure is unique: they can be deformed and return to their previous state.
The tissue complex of cartilage consists of chondrocyte cells and an extracellular matrix. Moreover, the cells are much smaller than the intercellular substance that surrounds them. Low regenerative abilities are associated with this very small number of cells.
There are only 1 to 10% of the total matrix volume. Worst of all is the pulpous nuclei in the intervertebral discs and articular cartilage. So that the matrix does not lose water, hyaluronic acid is present in it.
The intraarticular surface most often consists of hyaline cartilage, and half of its matrix is \u200b\u200bcollagen. If we study the structure of the collagen molecule under a microscope, we will see that these are large multilayer spirals. Therefore, they easily withstand stretching, tearing and twisting.
The articular cartilages were the least fortunate because they lacked blood vessels. Similarly, there are none in collagen cartilage. Water moves between the elements of the matrix and thus provides metabolic processes.
There is another kind of cartilage: the so-called fibrous or hyaline. It consists of our intervertebral discs.
Matrix viability depends only on chondrocytes. They synthesize all biopolymers: collagen, and elastin, and others.
The next problem is that if the cartilaginous tissue is immobilized, the synovial fluid will not be able to mix, and, therefore, the nutrition is disturbed and the mass of this structure begins to decrease. That is, any immobilization during fractures will adversely affect cartilage.
The last problem is that scientists have not yet been able to completely decipher the structure of chondrocytes to help them regenerate.
Cartilage alone can only be restored by half. Moreover, scarring often appears in place of normal tissue.
Now you probably think, my terrified reader, that it is absolutely impossible to revive the destroyed cartilage. However, it is not. How to do this, we will understand below.
Causes of destruction
As we explained above, age and numerous injuries are to blame. Here you can add the genetic predisposition, general metabolic problems, lack of vitamins and minerals in the diet, hormonal imbalance, some infectious and other diseases, but, most importantly, unbalanced loads.
What affects regeneration?
- Firstly, cartilage can be restored due to chondrocytes and matrix growth;
- Secondly, with the help of other varieties of connective tissue;
- Thirdly, bone cells initially have cartilage origin and are able to transform back and forth;
- Fourth, bone marrow can also be referred to such multifunctional cells.
After an injury, chondrocytes begin vigorous activity. The surge lasts about two weeks. However, the complete remodulation process will end only after a year. But the new fabric will be inferior in quality to the previous one.
What is the optimal treatment mechanism to choose?
When the acute period of the disease has passed, and inflammation and pain syndrome removed, the doctor’s task is to get rid of the damaged tissue. For this, specific enzymes and glucocorticosteroids are introduced into this zone by electrophoresis or ultrasound.
If cartilage is damaged only superficially, then potent pharmacological agents can help. After years of clinical trials, the highest activity was found only in the growth hormone, which activates the division of chondrocytes.
Sometimes it is combined with a thyroid hormone called thyrocalcitonin. However, the main disadvantage of such a hormone is that it cannot be administered locally.
When it is injected, the growth of all cartilage is activated, which is not always desirable. If you use it for a long time, then even the proportions of the skeleton may be violated.
They also make big bets on the insulin-like growth factor in the dosage form, it is responsible for the regeneration of all tissues in the body, including cartilage.
The doctor may prescribe daily administration of small doses of adrenaline, which also stimulates recovery processes.
 We already remember well that the weak regenerative functions of cartilage are due to a small number of chondrocytes.
We already remember well that the weak regenerative functions of cartilage are due to a small number of chondrocytes.
Therefore, it is not difficult to guess that at one point, doctors guessed to artificially introduce additional doses of chondrocytes into problem areas.
Moreover, the advantage of this manipulation is that the body, because of weak immunogenic activity, will not reject even foreign chondrocytes.
They gradually begin to multiply and form a new strong tissue. Cells of cartilaginous tissue of cattle that have died are used as donors. Embryonic material, which generally does not cause any immune rejection reactions, is best proven.
When even such global efforts do not produce any result, an artificial prosthesis is placed after surgery. At the moment, they are as close as possible to their prototype.
The next item is the favorite vitamins and minerals, but in this case they can really help.
How to change nutrition?
 Vitamin PP or nicotinic acid snatches our palm. Even small doses of this substance that enter the bloodstream can increase the level of growth hormone by two or three times. Vitamin K can also be mentioned in this list.
Vitamin PP or nicotinic acid snatches our palm. Even small doses of this substance that enter the bloodstream can increase the level of growth hormone by two or three times. Vitamin K can also be mentioned in this list.
The state of the matrix is \u200b\u200bchanged for the better by overdoses of ascorbic acid. It is usually combined with vitamin P.
Beneficially ascorbic acid also affects collagen structures.
Among others, a combination of ascorbic acid with glycine or with proline, alanine and lysine is used.
Restoration of cartilage with folk remedies
 These products are advised for healing bones even in “Homebuilding”.
These products are advised for healing bones even in “Homebuilding”.
You can even find exotic recipes such as chicken cartilage diluted in orange juice.
Among other things, you should eat sea fish and other seafood, as well as dairy products, which are rich in calcium and phosphorus.
As we already explained above, a meal containing high doses of the indicated vitamins will be really effective. This is almost all raw vegetables and vegetable oils.
In general, a positive review of the diet in any case will bring you undeniable benefits.
Your spine and the whole body will thank you if you restore the intestines, learn to eat only healthy and balanced food, and, most importantly, cook it. Excellent recommendations and detailed instructions on this topic can be found here: Free Special Report " 10 essential nutritional components for a healthy spine"

There you will find answers to many questions that I did not manage to reveal today in my story.