Bowel problems accompany a person all his life. It is scientifically proven that 90% of all diseases occur due to a malfunction in the intestines.
Often people turn to specialists for help not at the initial stage, but when the disease begins to pass into the chronic stage. After all, intestinal diseases are a very delicate topic, it is not accepted to discuss it.
Many people try to cure diseases of their intestines by finding symptoms. Treatment is carried out with the help of yogurt.
The use of dairy products is useful, but it is impossible to cure the pathology. A specialist in such diseases (gastroenterologist) will identify the cause, make a diagnosis, prescribe competent treatment.
Bowel diseases are diverse, have their own characteristics, only a doctor will be able to understand the problem.
For diseases characteristic different signsbut there are common symptoms of the disease in the intestines:
- pain in the abdomen;
- stool disorders;
- increased gas formation, rumbling.
The intestine plays a large role in the digestion of food, providing the body with useful substances. That's why diseases in the intestines can affect any internal organ and system.
Manifestations of pathological changes are hardly noticeable, for some period of time they can even disappear. But the disease will gain strength and manifest more powerful. One of the main causes of bowel disease is malnutrition.
A sedentary lifestyle also provokes painful changes in this organ. The best thing a person can do for his health is to consult a doctor in time for making a diagnosis.
Features of pathologies of the small intestine
In the process of digestion, the small intestine is of great importance. Processing processes end in its cavity, the assimilation of nutrients begins.
Diseases of the small intestine are associated with these two functions. Absorption may be impaired or normal digestion may fail.
Signs of pathological disorders have standard manifestations.
Symptoms of small bowel disease:
- soreness is localized around the navel;
- rumbling, increased gas formation in the abdomen is characteristic for the second half of the day, by night the appearance is reduced;
- patients suffer from diarrhea, in the feces visible residues of undigested foods;
- due to poor absorption of nutrients, weight loss, hair damage, dry skin, brittle nails, disruption of the internal systems of the body begin.
All symptoms are acute, then go into the chronic stage, slightly weakening.
Enteritis
This is an inflammatory disease of the small intestine that provokes dysentery bacillus, salmonella, rotaviruses and other pathogenic microorganisms.
The cause of this inflammatory process may be the effect of drugs, for example, antibiotics. Also, the effect of ionizing radiation provokes enteritis, heavy metals, for example, lead, arsenic.
Symptoms of the disease are:
- weight loss;
- hair loss;
- intolerance to dairy products;
- pain in the navel;
- bloating, unpleasant rumbling;
- upset stool - diarrhea.
At the consultation with a specialist, additional examinations are prescribed. According to their data, a diagnosis is established, the stage of damage to the small intestine is determined.
Celiac disease
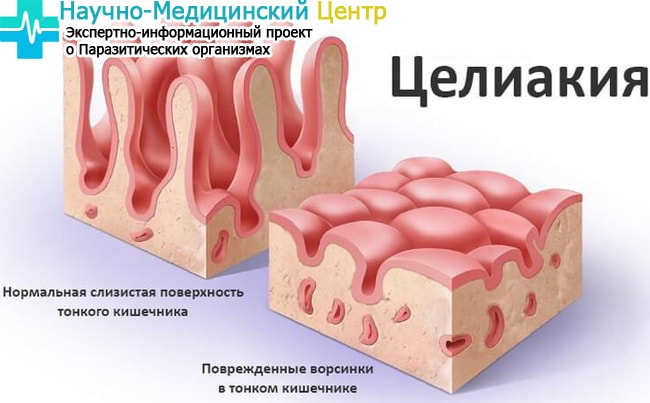
This pathology is also called gluten enteropathy. The reason is a congenital deficiency of a certain enzyme that breaks down gluten (it is part of the protein in all grains).
Residues from incompletely digested protein negatively affect the small intestine. Its cells exfoliate, the mucous membrane becomes thinner, can no longer perform its functions - processing and assimilation are disrupted.
Symptoms of the disease:
- severe diarrhea;
- sharp loss of body weight;
- bruising on the skin;
- bleeding gums;
- sore bones, fractures are possible;
- in severe cases, mental abnormalities are observed.
Manifestations of celiac enteropathy are confused with similar diseases. Diagnose pathology can only be a good specialist.
Often the diagnosis is made when the disease is already becoming chronic. Patients with such a disease have to follow a strict diet all their lives, but this makes it possible to maintain health.
Whipple's disease
The disease is rare, not only the small intestine, but also other internal organs are affected.
The cause of the pathology is carinobacteria. Their life activity is accompanied by inflammation, in which specific macrophage cells settle in the intestines and lymph nodes. They block the absorption process in the intestines.
Symptoms of the disease:
- heat;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- sharp weight loss;
- pain throughout the abdomen by type of contractions;
- redness, swelling of the joints;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The diagnosis is made after examination, additional tests. It is necessary to treat this disease for a long time, but the prognosis for recovery is favorable, the functioning of the intestine is restored.
Tumors
In the small intestine, tumor processes are rare. Usually these are benign neoplasms. Symptoms of such pathologies depend on whether the tumor remains in place or is distributed further along the mucous membrane.
When the neoplasm increases at a certain place, then the intestinal lumen narrows over time, which means that symptoms of intestinal obstruction will appear:
- cramping, abdominal pain;
- vomiting
- bloating;
- diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- anemia.
To clarify the position of the tumor in the intestine, an X-ray examination is usually prescribed. If a tumor is detected, they are removed from it by surgery or chemotherapy.
Features of the pathology of the large intestine
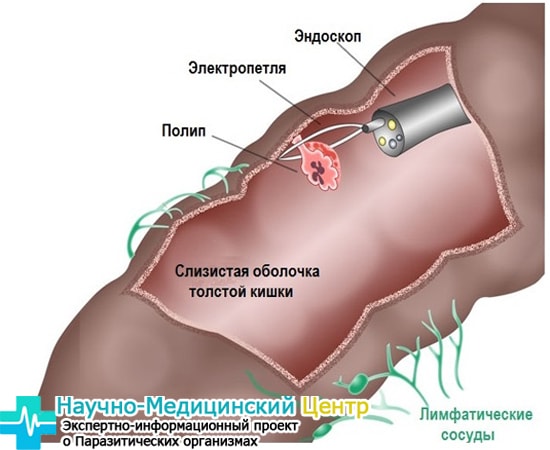
Disturbances in the work of the large intestine are always accompanied by disorders of the stool, but constipation is more often noted. Diarrhea occurs at the stage of exacerbation of the disease. In the masses of feces, blood, mucus can be observed.
Pain is more often noted in the lateral abdomen, in the anus, but around the navel is very rare. When the doctor feels the abdomen, the pains appear on the left and right under the ribs.
Soreness in the abdomen is not associated with eating, but increases with the use of milk, a large number of fruits. After defecation, the pain decreases. A warm heating pad and some enzyme medications also help with pain.
A rumbling in the abdomen and increased bloating is noted in the evening hours, and by night the abdomen usually calms down. Prolonged constipation provokes poisoning of the body, so the symptoms will be characteristic.
Signs of a disease of the large intestine:
- bad sleep;
- nervousness;
- depressive state;
- increased anxiety.
And weight loss, diarrhea, anemia are characteristic for lesions of the small intestine.
Colitis (ulcerative)
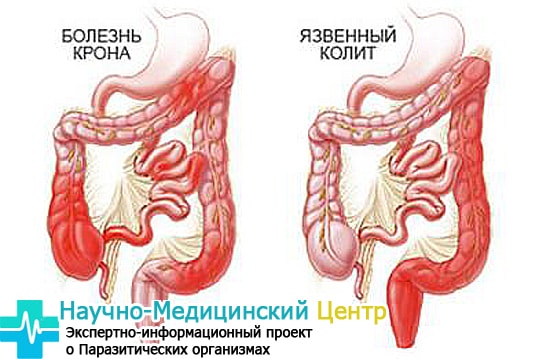
This inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon occurs in a chronic form with exacerbations. The causes are disorders in the immune system, they can be hereditary.
The mucous membrane is covered with numerous ulcers, erosion sites. A prolonged course of the disease can provoke the occurrence of polyps, neoplasms of the large intestine.
Symptoms of this disease will be:
- blood in the stool;
- frequent stool disorders;
- soreness of the left half of the abdomen;
- weakness;
- weight reduction.
To clarify the diagnosis, the mucosa is examined with a special device - a colonoscope. With ulcerative colitis, the mucous membrane has characteristic changes.
Ischemic colitis
The disease is an inflammatory process that forms due to vasoconstriction. The nutrition of the intestinal wall is disturbed (ischemia), which leads to the formation of ulcers, in the future, a serious narrowing of the intestinal lumen may occur.
The causes of this pathology are vascular damage, diabetes. Often the disease manifests itself in old age.
Symptoms
- soreness of the left half of the abdomen not immediately after eating;
- traces of blood in the stool.
Symptoms of this bowel disease are clearly manifested in the first phase of development, then gradually weaken. Over time, the disease will manifest itself again, so you need to be wary when blood is noticed in the feces.
Early treatment for medical help will make it possible to quickly diagnose and begin treatment.
Tumors in the colon
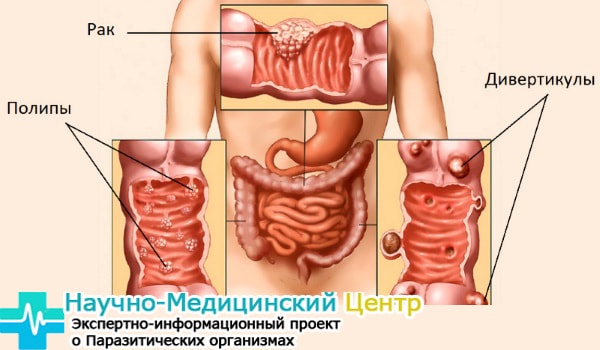
Currently, malignant neoplasms of the large intestine are often diagnosed. This type of disease provokes malnutrition, the use of refined products. An intestinal tumor can occur as a complication of polyps, colitis, and other diseases of this area.
The difficulty in treating such bowel diseases is that the symptoms are already evident in the later stages. For example, polyps may not appear at all, they will be discovered by chance during an X-ray examination. The tumor can also be found unexpectedly.
If neoplasms are located on the left side, then the symptoms will be of a general nature of intestinal obstruction:
- pain in the abdomen in the form of contractions;
- blood in the stool;
- constipation.
With polyps or a tumor in the right intestine, the signs will be more general:
- heat;
- diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- general weakness.
Such signs of the disease should prompt an examination. Indeed, at an early stage, pathology is easier to cure, faster.
Large intestine dyskinesia
With this disease, the motor function of the organ is impaired. Perhaps a separate disease or complication after a pathology of the gastrointestinal system. The basis of a failure of the motor ability of the colon is often stressful situations, depressive states, high anxiety on everyday problems.
Intestines are provoked by past infections, an allergy to some foods, an unbalanced diet, in which there are few indigestible substances. Long-term dysbiosis increases the likelihood of developing dyskinesia.
Symptoms are:
- strong rumbling, not tied to the use of any product (may be the only symptom);
- soreness of the abdomen, but it is difficult to determine the place and type of pain;
- diarrhea and constipation alternate;
- pains are noted in the back, heart, even in the joints, although there are no diseases of these organs.
The picture of the disease is often blurred, additional tests and examinations will be required to confirm the diagnosis.
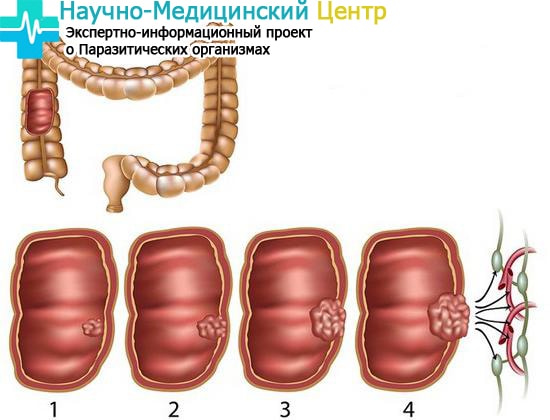
Diverticulosis
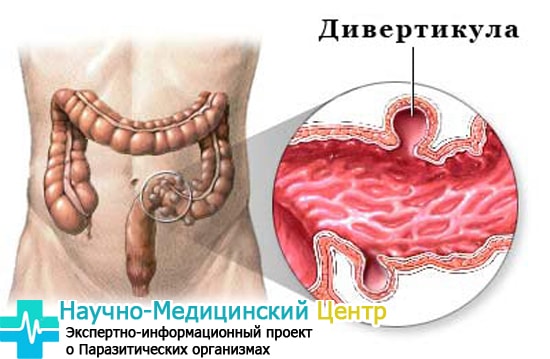
In a sick person, small protrusions are formed in the intestines, which are called diverticula. Residents of economically developed countries are most affected by such changes in the internal organ.
Every third resident of a large metropolis has a predisposition to such a disease. The whole problem is that products with fiber, coarse plant fibers disappear from the diet of a modern person. Such a diet leads to constipation, and this is a direct risk of developing diverticulosis.
At the initial stage, intestinal, like others, the disease does not manifest itself. May be disturbed by minor stool disorders, mild pain throughout the abdomen. Explicit manifestations begin when the content of the diverticulum is disrupted.
The signs will be:
- heat;
- diarrhea;
- mucus and blood in the stool.
The main danger of this condition is intestinal bleeding, the likelihood of which increases with age. The diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray examination. It is important not to start the disease before the stage of narrowing of the intestinal lumen, it is very difficult to treat such a condition.
In this disease, prevention plays an important role. Nutrition should be balanced, contain a sufficient amount of substances necessary for the intestines. To do this, regularly eat fresh vegetables and fruits. You also need to constantly monitor bowel movements, notice the slightest deviations, and visit a doctor in a timely manner.
Rectal problems
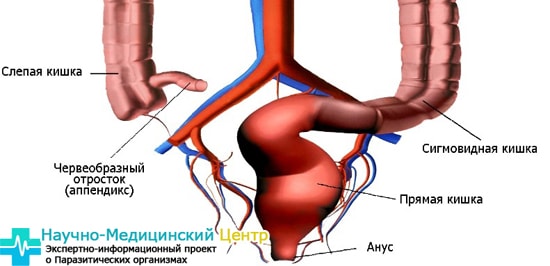
Symptoms of a rectal disease may not appear very clearly. There are asymptomatic or very mild symptoms. Many diseases of this part of the intestine are accompanied by metabolic disorders, which is manifested by general fatigue, slow growth, and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Standard signs of rectal pathologies are:
- soreness of the abdomen and anus;
- pus in the stool;
- an admixture of blood in the stool;
- persistent constipation;
- flatulence of the abdomen with gas.
With blood loss, anemia often develops. Symptoms of a manifesting bowel disease are often similar to other pathologies, so a specialist can establish the correct diagnosis after a comprehensive examination.
Hemorrhoids
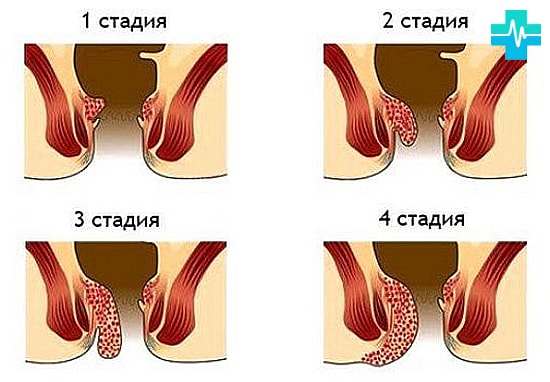
Unpleasant pathology, which is gaining unprecedented scope in modern society. Hemorrhoids are the expansion of veins in the rectum with the formation of specific nodes.
The causes of hemorrhoids can be a sedentary lifestyle, pregnancy, lack of fiber in food.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids:
- itching, discomfort in the anus;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- traces of blood during bowel movements or on linen, toilet paper;
- in the later stages, the patient can feel for the fallen node with his hand and even set it in place.
The main mistake in this disease is a late call to a specialist when good opportunities for treating the disease are missed.
There are effective methods of treating hemorrhoids that can quickly relieve a person of suffering. But the disease is considered delicate, those who are sick are embarrassed to visit a doctor. Over time, the situation worsens, it can lead to surgery, because there is a risk of pinching of the dropped nodes.
Crack
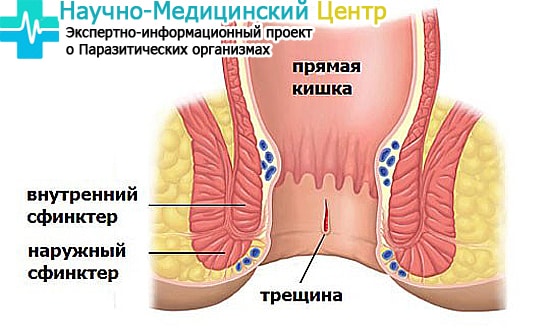
A small anal fissure appears on the wall of the anus. At first, this happens as an ordinary tear of the skin, which changes during a chronic course - the edges begin to harden, the surface is covered with dense tissue. Various diseases of the intestine, of all its departments, can provoke the appearance of a crack in the anus.
The crack will be manifested by pain and bleeding. Moreover, the pain can be very severe, lasting several hours after bowel movement. In some cases, it is impossible for a sick person to sit, it is difficult to walk, for example, to climb stairs. It is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, over time, the disease will only develop, and the pain will intensify.
Conclusion
There are many diseases of the intestines, the main symptoms are known. With persistent manifestations of pathology, you should immediately seek medical help.
Modern methods of medicine help efficiently, quickly. But nevertheless, dietary nutrition is of great importance for recovery. The doctor will advise which food system to follow in order to improve the bowel condition. Getting rid of constipation will bring noticeable relief.
Modern life is becoming more comfortable, but it is unnatural for the human body. A sedentary lifestyle provokes diseases of the spine, heart, intestines.
If a person does not change the order of his life, then no medicine will help him. Feasible exercise stress, normal physical activity are able to keep the human body healthy for many years.
And bloating. Attacks of diarrhea occur 3 to 6 times a day, while the stool is very different from the usual one: you can see undigested food in it, but there are often no traces of mucus or blood. Bloating and rumbling mostly torment the patient in the afternoon. Often there are pains in the lower abdomen on the right side or near the navel.
A rather characteristic symptom is extraintestinal signs of the disease. There are a lot of them, but basically all of them are explained by a violation of the digestion of food and, as a result, by the termination of the absorption of useful substances by the body, such as minerals, vitamins and salts. The patient can lose weight very sharply and continue to lose weight, inflammation of the oral cavity, tongue, dry eyes, anemia, and seizures (angular stomatitis) may develop. The work of the endocrine glands is disrupted, as a result of which the menstrual cycle can change in women and impotence can develop in men.2 Diseases of the most important gastrointestinal tract
- Enteritis.
Chronic enteritis is one that is accompanied by impaired function. The causes are causative agents of acute intestinal diseases. Moreover, in the chronic stage of the disease, these pathogens are already absent (post-infection process). Development mechanism: bacteria enter the small intestine, where healthy people cannot have them; there is dysbiosis, which subsequently leads to a disruption in the production of intestinal enzymes and weakening of the body's defense system. The motor function of the small intestine is also impaired.
Signs of chronic enteritis are divided into subgroups:
- local intestinal manifestations (rumbling in the abdomen, pain around the navel, bloating, diarrhea);
- general symptoms (sudden weight loss and inability to gain weight, impotence in men or menstruation in women).
There are so many ways to detect this disease, mainly they are carried out by a gastroenterologist. After passing the examination, not only the result becomes known, but a certain treatment is prescribed, depending on the severity of the disease.
- Intolerance to some carbohydrates.
Some people have such a feature as the lack of special enzymes in the body that can break down carbohydrates. For example, many people have problems using cane sugar, dairy products with lactose, or mushrooms. For the breakdown of the carbohydrates contained in these products, certain enzymes are responsible that may not be present in the human body from birth. Most common. It occurs when dairy products are eaten, manifested by rumbling in the abdomen, diarrhea, bloating, and sometimes sharp pulling pains. A gastroenterologist can recognize this disease, who, with the help of certain tests, must determine with accuracy whether it is the absence of enzymes or a simple allergy to foods.
- Vascular disease of the small intestine.
Blood comes from three large arteries that extend from the abdominal cavity, directly into the small intestine. With vascular disease, blood begins to flow to the intestines in smaller quantities. Basically, this disease is combined with atherosclerosis of blood vessels of other areas - the brain, heart, limbs. As a result, a vascular disease develops, which in common people is called abdominal toad.
The initial sign of the development of the disease is severe abdominal pain that occurs about an hour after eating. Sometimes they can be so heavy that a person refuses to eat, and as a result pretty quickly loses a lot of body weight. Along with this, bloating, a violation of the stool may be present. If any of the symptoms is detected, you should immediately consult a gastroenterologist.
They are very similar, therefore, sometimes doctors are looking for a stomach, but if a negative result is obtained, then a thought may arise about a problem with the vessels, so you can’t delay it - it’s better to initially identify the problem and timely treat it. Vascular diseases are very dangerous, because if the necessary measures are not taken in time, the vessels can become completely clogged, which will lead to the development of intestinal infarction.
The patient is prescribed a special diet, in which food must be taken 6 times a day in small portions. Of the drugs, vasodilators and enzyme preparations are mainly prescribed. If other treatment methods do not show positive dynamics, then doctors perform an operation in which old vessels are replaced.
- Whipple's disease
 This disease is considered quite rare, during its development and progression, not only the small intestine, but also other organs can suffer. The reason for the development is the ingestion of special bacteria called corinobacteria into the small intestine. After their penetration in the organs, the inflammatory process begins. Lymphatic tissues, intestines and other organs are literally flooded with macrophages (special cells) that block the lymphatic vessels, as a result of which they are filled with fat. This leads to disruption of the absorption process. The patient's body temperature rises, the joints swell and redden, he loses weight very quickly, all groups of lymph nodes increase, and cramping pains appear in the lower abdomen.
This disease is considered quite rare, during its development and progression, not only the small intestine, but also other organs can suffer. The reason for the development is the ingestion of special bacteria called corinobacteria into the small intestine. After their penetration in the organs, the inflammatory process begins. Lymphatic tissues, intestines and other organs are literally flooded with macrophages (special cells) that block the lymphatic vessels, as a result of which they are filled with fat. This leads to disruption of the absorption process. The patient's body temperature rises, the joints swell and redden, he loses weight very quickly, all groups of lymph nodes increase, and cramping pains appear in the lower abdomen.
To establish the correct diagnosis and not to confuse the symptoms, the specialist conducts special studies of the mucosa.
- Tumors
In the small intestine, they are extremely rare. In most cases, the tumors are benign, and lymphomas or cancer are rarely seen. The disease manifests itself with sharp pains around the entire perimeter of the abdomen, vomiting and bloating occur, since the emerging tumor complicates the flow of blood. This disease must be urgently treated. Symptoms that occur once will only progress.
3 Allergic reactions
In an allergic reaction, damage to the small intestine can be either a component of the general reaction of the body to an allergen, or an independent manifestation. Enteropathy is mainly the result of exposure to drugs, food antigens, or a reaction to plant pollen.
 Symptoms of allergic reactions:
Symptoms of allergic reactions:
- cramping pains;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- constant urge to the toilet;
- increase in body temperature;
- nausea.
Often, the deterioration is associated with the use of a particular drug or food product. But basically, these symptoms are combined with other manifestations of allergies (itching, skin rashes). It is quite difficult to make a diagnosis in such a situation; these unpleasant sensations require examination by a specialist.
Treatment can be greatly facilitated, if you find the reasons - to identify an allergen. Here you can go by the method of exception - of course, under the supervision of a doctor.
4 Treatment of diseases
Treatment of diseases of the small intestine is a rather difficult task (due to the similarity of symptoms), but it is quite feasible. The patient is required only to comply with the doctor’s prescriptions, a little perseverance and patience, as well as a certain diet.
 For all problems with the small intestine, you can eat:
For all problems with the small intestine, you can eat:
- bakery products;
- vegetable soups;
- boiled or steamed meat or fish;
- mashed potatoes, casseroles and other side dishes made of vegetables;
- pasta, cereals;
- eggs
- fruit;
- milk.
The second and most important treatment is exposure to dysbiosis. The purpose of the exposure is to normalize the intestines. For this, a specialist doctor prescribes antimicrobial drugs to the patient. After a course of these drugs, when all the most aggressive microbes are supposedly suppressed, bacterial drugs are prescribed for the patient. They contain good, beneficial microbes that are present in every person’s healthy intestines. These are our assistants, they protect and ensure the normal functioning of the small intestine.
During the disease, the intestines reduce the production of enzymes that guarantee the normal absorption of nutrients. Therefore, the patient is prescribed a course of enzymes and vitamins in order to restore vitality to the body.
Diagnosis of the disease is a rather complicated task, which only a gastroenterologist can handle. It is almost impossible to independently identify the cause, unless the patient has certain knowledge in medicine. If there is and there is a likelihood that this concerns the intestines, the symptoms will not help to accurately determine the cause of their occurrence. Therefore, it is necessary to hurry to the doctor in order to identify the disease in time and begin treatment. You can never bring the disease of this sphere to a chronic stage - because it is easier to get rid of a problem when it first appeared.
The small intestine has a very responsible role in the digestive system of the human body. He is responsible for the digestion of food, the absorption of nutrients that are needed for the construction of cells, tissues. When the symptoms and signs of the disease arise, they are pretty uniform. Almost all diseases of the small intestine are covered by the concept of "malabsorption". They are also known as "malabsorption syndrome."
To enlarge a picture, click on it with the mouse.
Gastroenterologist Mikhail Vasilievich:
"It is known that for the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, etc.), there are special drugs that are prescribed by doctors. But we will not talk about them, but about those drugs that can be used on their own and at home ..."
Description of the disease
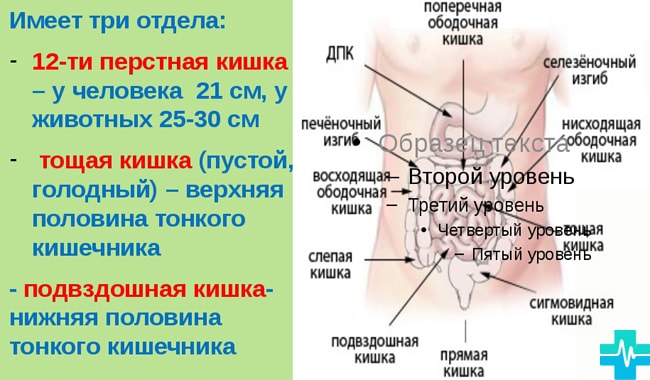
The small intestine is located between the stomach, colon. It is on this site that the most important digestion processes take place. The small intestine includes such departments:
- duodenum. It is the initial part of the small intestine. It begins immediately after the stomach. It is associated with such digestive glands: liver, pancreas, gall bladder;
- jejunum. It is represented by the middle part of the small intestine. This site is located between the duodenum, ileum. The loops of this gut occupy a place in the upper left abdomen;
- ileum. It is the lower part of the small intestine. This area begins after the jejunum, it ends in front of the cecum. This site has thick walls, large diameter, many vessels. It is located on the lower right abdomen.
Pain in the small intestine occurs with such pathologies:
- maldigestion syndrome;
- crohn's disease;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- enteritis;
- celiac disease;
- intestinal obstruction;
- malabsorption syndrome;
- intestinal dyskinesia;
- duodenal ulcer;
- tumor of the small intestine;
- intestinal diverticula, intestinal inversion;
- ischemia, intestinal infarction.
Symptoms

If the small intestine is affected by any disease, the following symptoms appear:
- pain localized in the navel;
- transfusion in the abdomen, which the patient can feel or hear;
- loose stools (the color is light, it is mushy, foamy, interspersed with undigested products may be observed, the smell is sour, unpleasant);
- bursting of the abdomen;
- an increase in temperature (noted in inflammatory bowel diseases. The height of the thermometer depends on the number of microbes, their toxicity, and body resistance);
- peremptory urge to defecate;
- feeling of heaviness;
- bloating.
Let us consider in more detail the symptoms that arise with specific pathologies of the small intestine.
Enteritis
Enteritis is represented by inflammation of the small intestine. Depending on where the inflammation is localized, duodenitis (12 duodenal ulcer), ileitis (ileum), and unititis (jejunum) are isolated.
In acute enteritis, the following are manifested:
- vomiting
- diarrhea;
- sharp pains (sudden);
- heat;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- dehydration;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- intoxication.
If chronic enteritis develops, manifest:
- diarrhea;
- vomiting
- weakness;
- nausea;
- persistent epigastric pain (unsharp);
- decreased appetite;
- pain on palpation, manifested deep in the area above the womb;
- feeling of fullness;
- rumbling inside the intestines.
Crohn's disease
This chronic inflammation of the digestive tract can affect all layers of the digestive tube. The disease can provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes of the peritoneum, the appearance of ulcers, scars on the walls of the intestine. With the disease, the following symptoms appear:
- nausea, vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- bloating;
- diarrhea;
- loss of appetite, weight;
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- temperature rise.
Duodenal ulcer
The main symptom is pain. It is insignificant, stitching, sucking, cramping. This pathology is characterized by "hungry pains."
Intestinal obstruction
This pathology is represented by a complete / partial violation by the movement of food along the digestive tract. A constant symptom of the disease is pain that appears suddenly, not dependent on food intake.
In addition to pain, you may see:
- bloating;
- asymmetry of the abdomen;
- vomiting
Intestinal dyskinesia
This violation of the motor functions of the small intestine is manifested in:
- abdominal pains;
- increased production of mucus;
- feeling of pressure, heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- colic
- constipation
- diarrhea.
Diverticulum
With this saccular protrusion of the submucous, mucous membranes of the intestine appear:
- heat;
- acute abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- tension of the peritoneal wall;
- violation of the stool.
Dysbacteriosis
This pathology is manifested in a violation of the quantity, quality of the normal intestinal microflora. The patient appears:
- weakness;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- malaise;
- headache;
- decreased performance;
- pallor of the dermis.
Malabsorption syndrome
This pathology is manifested in insufficient absorption of nutrients into the small intestine. The main symptom of the disease is loose, mushy stools. It is foamy, practically does not contain mucus. Also, the patient is worried:
- bloating;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- flatulence;
- muscle pain;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- lowering blood pressure;
- anemia;
- losing weight;
- numbness of fingers, lips;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- burping.
Maldigestion syndrome
This clinical symptom complex is caused by impaired digestion of nutrients. It manifests itself with a lack of digestive enzymes, pathology of the small intestine.
With this disease, there are:
- pains pulling, bursting in nature (they are provoked by increased pressure inside the intestine);
- upset stool (diarrhea prevails);
- flatulence;
- rumbling, bloating;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- burping.
Celiac disease
This pathology is hereditary. It manifests itself in intolerance to products that contain gluten (rye, barley, wheat, oats).
When using complementary foods containing flour products, children manifest:
- lethargy;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- pallor;
- mucous membranes become bright;
- the size of the abdomen increases.
You may also see:
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- dry dermis;
- stomatitis;
- iron-deficiency anemia;
- pain in the intestines, having a aching, pulling character;
- diarrhea (defecation foamy, has a pungent odor. Its color is light, grayish, consistency is characterized by increased fat content).
Ischemia, heart attack
These pathologies are manifested in a chronic violation of the blood supply to the walls of the intestine. The main symptom is severe abdominal pain. In addition to pain in the navel area, the patient has:
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bloating, rumbling of the abdomen;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- pain when palpating the abdomen;
- the presence of blood impurities in the bowel movement.
Bowel cancer, tumors
Pain with this pathology is mild. It is difficult to indicate their exact location. The main symptoms of pathology:
- loss of appetite;
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- severe depletion of the body.
The following diagnostic methods will help the specialist find the cause of the disease:
- Ultrasound of the abdomen.
- CT scan.
- Radiography of the peritoneal organs.
- Bacteriological examination of feces.
- Endoscopic examinations (FEGDS, colonoscopy).
- Histological studies. They are needed to clarify the nature of the pathology (benign, malignant tumors).
Treatment
If any disease affects the small intestine, symptoms will appear that the patient will be very difficult not to notice. If there is a violation of the stool, characteristic abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, headaches, flatulence, belching, you need to seek specialized help.
The treatment of diseases that arose in the small intestine is considered a rather complicated process. The main thing is that in the process of treatment, strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and follow the prescribed diet.
An important point in the treatment of diseases of the small intestine is the effect on dysbiosis. Therapy is aimed at normalizing bowel function. The patient should take antimicrobial drugs.
Vitamin therapy, a course of enzymes are also very important. This is necessary to restore the strength of the body. Enzymes are necessary for the normal absorption of nutrients.
Also, the doctor needs to reduce inflammation, reduce intoxication of the body. In the treatment of infections, inflammations, the following medicines are used:
- antibacterial drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- immunomodulating medications.
If drug therapy does not give the desired results, the doctor decides on the use of surgical intervention. During the operation, specialists remove the affected areas of the intestine.
Estimated treatment prices in the main centers
| City name | Medical facility | Procedure | Price |
| Volgograd | Volgograd Regional Clinical Hospital № 1 | 327 rub | |
| Kharkiv | Olympic | Gastroenterologist appointment | 120 UAH |
| Ekaterinburg | SMT Clinic | Reception specialist | 1500 rub. |
| SPB | Expert | Gastroenterologist appointment | 1000 rub |
| Alma-ata | Onclinic | Specialist Admission Cost | 5600 tenge |
| Samara | Arctic | Gastroenterologist examination | 800 rub |
| Permian | Alpha Health Center | Primary specialist appointment | 964 rub. |
| Novosibirsk | Medical On Group | Primary appointment | 1100 rub. |
| Chelyabinsk | Pearl | Specialist examination | 780 rub. |
| MSC | Kindred | Specialist consultation | 1500 rub. |
| Nizhny Novgorod | Alpha Health Center | Gastroenterologist appointment | 161 rub |
| Kiev | EUROMED | Specialist consultation | 250 UAH |
| Odessa | Onclinic | Primary specialist appointment | 200 UAH |
| Omsk | Clinical Diagnostic Center on Ilyinskaya Street | Gastroenterologist consultation | 600 rub |
| Dnepropetrovsk | OH Clinics Dnipro | Gastroenterologist appointment | 250 UAH |
Prevention

You can avoid the occurrence of many diseases of the small intestine. To do this, it is enough to observe elementary actions:
- Healthy food.
- Avoid stress, nervous breakdowns.
- Eat quality, fresh food.
- Do not abuse alcohol, tobacco.
- Do not trigger pelvic disease (women).
- Keep clean food consumed (vegetables, fruits).
- To live an active lifestyle.
- The disease is desirable to detect in a timely manner. This contributes to the speedy cure of pathology.
- Drug therapy will be effective if you follow a diet, rest the body from emotional, physical stress.
- To recover, you need a balanced, fractional diet.
- It is recommended to take vitamin preparations with calcium, iron.
- It is important to observe the drinking regimen. A patient should drink from 2 liters of water per day.
- It is necessary to abandon foods that contain a lot of fiber, foods that have a high glycemic index. Fried, oily should be excluded, it will limit the consumption of lactose.
Tired of stomach pain, stomach pain ...?
- i have a stomachache;
- vomiting
- diarrhea;
- heartburn;
Forgot when you were in a good mood, and even more so when you feel good?
Yes, digestive problems can seriously ruin your life!But there is a solution: gastroenterologist, head of the gastroenterological department Arkhipov Mikhail Vasilievich
The intestine is the longest human organ, which in an adult is about four meters. It is divided into two main parts - the colon and small intestine, and this structuring is not conditional, since both of these parts perform different functions.
The doctor may indicate the approximate localization of inflammation according to complaints
So, in the small intestine under the influence of pancreatic enzymes, food is broken down and absorbed; the fat one is engaged in "packing" the spent food masses, taking away excess water from there. Symptoms of intestinal inflammation - the most common of its diseases - will differ depending on the localization of the process, because it will be seen what function has suffered.
Terminology
Inflammation of the small intestine is called enteritis, and if the process is located only in its final part - the ileum, then the disease will be called ileitis.
When the inflammatory process is localized in the colon, then this is called colitis. If the pathology concerns only the sigmoid colon, it is called sigmoiditis, if the rectum is proctitis.
Why the intestines become inflamed
The causes of intestinal inflammation are conventionally divided into two large groups: infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious Enterocolitis
To infectious include various:
TIP! Get rid of the dark circles around the eyes in 2 weeks.
- viruses: enteroviruses, adenoviruses and others;
- bacteria: cholera vibrio, salmonella, pathogenic E. coli, shigella (it causes dysentery), staphylococcus (especially its subspecies called "golden"), halophilic and other microorganisms;
Such microorganisms get into with unboiled water and milk (as well as when swallowing water when bathing), poor-quality or not heat-treated food. Viruses are able to get through the airborne droplets.
The peculiarity of infectious inflammatory processes is that they are contagious and can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through common dishes, food, toys and household items. They are called “diseases of dirty hands”, since it is quite simple to avoid infection: wash your hands after talking with the patient, before eating and after visiting the toilet shared with him.
Intestinal inflammation not associated with microbial colonization
Non-infectious intestinal inflammation develops due to a huge number of causes. It:
TREAT THE REASON, NOT THE CONSEQUENCE! Natural Ingredients Nutricomplex restores the correct metabolism in 1 month.
- errors in: “love” of alcohol, spicy and smoked food;
- decreased bowel tone;
- inflammation of nearby organs;
- taking medications;
- “Defects” of immunity, in which he begins to “attack” his own organs (such an autoimmune process is characteristic of Crohn’s disease);
- violation of the blood circulation of the intestine due to atherosclerotic or inflammatory processes in the arteries that feed it;
- poisoning with lead, heavy metals, arsenic, poisons from plants;
- food allergy;
- irradiation of the intestine with gamma rays;
- as a reaction to surgery on the abdominal organs.
How is intestinal inflammation manifested?
General symptoms of inflammation of the intestinal mucosa can be divided into the following syndromes:
- Painful. The localization of inflammation can be assumed by the location of the pain zone:
- if it hurts in the navel, this most likely indicates a disease of the small whether the initial sections of the large intestine;
- pain in the lower parts - a disease of the colon;
- in the anus - rectal problems. This is not necessarily inflammation, it can be a symptom of hemorrhoids, and anal fissure.
- By the nature of the pain:
- if the pain is constant, aching, the process is chronic;
- if it has a daily rhythm: amplifies in the first half of the night - ulcerative pathologies, in the morning - inflammation of the large intestine;
- when the pain intensifies with shaking, bowel movements, walking, it says that the peritoneum or lymphatic system of the intestine is involved in the inflammation.
- Intoxication syndrome: weakness, drowsiness, increased heart rate, nausea, decreased appetite, muscle pain, headaches. This is in favor of the infectious process.
- Diarrheal syndrome (diarrhea) can indicate both small intestinal and colonic localization. The type of feces matters.
- Dry hair and skin, seizures in the corners of the mouth, bleeding gums indicate problems with the small intestine.
- Change in color and stool consistency.

To determine the localization of inflammation, it is important to indicate not only the pain zone, but also other symptoms
Consider separately the symptoms of diseases of the large and small intestines.
Enteritis
Inflammation of the small intestine can be acute and chronic.
IMPORTANT! How to remove bags and wrinkles around the eyes in 50 years?
Warning! Acute inflammation often has an infectious nature, and also develops in case of poisoning or an allergic reaction. The cause of chronic enteritis is most often diet errors.
For the prevention and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, our readers recommend Monastic tea. This is a unique remedy which includes 9 medicinal herbs useful for digestion, which not only complement, but also enhance the actions of each other. Monastic tea will not only eliminate all the symptoms of gastrointestinal tract and digestive organs, but also permanently relieve the cause of its occurrence.
The opinion of readers ... "Symptoms of acute enteritis
The disease usually begins acutely, with the appearance of such symptoms:
- weakness;
- rumbling and pain in the abdomen, in the navel;
- diarrhea: up to 10 times a day;
- stool: liquid, foamy, fetid;
- decreased appetite;
- dry skin;
- most likely, there will be an increase in temperature;
- signs of dehydration may develop: severe weakness, confusion, cramps, frequent weak pulse.
Chronic enteritis
With this disease, frequent loose stools are observed, which is accompanied by abdominal pain and rumbling of the intestine - during an exacerbation. In the period of remission, a decrease in the severity of these complaints is noted until their complete disappearance. The fact that the disease is not stopped is evidenced by the signs of a disturbed intake of nutrients in the body: dryness, brittleness and thinness of the skin, hair and nails, seizures, pallor, bleeding.
Colitis
Inflammation of the large intestine is also acute and chronic. Chronic colitis, depending on the nature of the inflammation in the intestine, has its own classification. All these pathological processes have different symptoms.
Acute colitis
It is characterized by such signs:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- painful urge to defecate;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- feces - formed, mucus and blood are visible in it;
- with infectious bowel disease - an increase in temperature.
Chronic ulcerative colitis
This is the name of the process in which ulcerative and erosive defects occur in the wall of the intestine. It develops more often in women and is characterized by such manifestations:
- abdominal pain, especially on the left side;
- constipation
- during the stagnation of the disease, feces are not liquid, fetid, blood is visible in it;
- with exacerbation, abdominal pain, diarrhea are noted, a person quickly loses body weight;
- joint pain often develops.
Warning! Under the symptoms of intestinal inflammation in women, diseases of the reproductive organs can be masked: pain in the right or left half of the abdomen can also be observed with inflammation of the appendages; diarrhea can accompany not only colitis or enteritis, but also inflammation of the uterus and appendages. Only a doctor can figure out the causes of symptoms.
Chronic spastic colitis
It has different manifestations: one person may develop constipation, while another has diarrhea. Most people also have abdominal pain, flatulence, bloating. Spastic colitis is characterized by the disappearance of symptoms during the relief of nervous strain, stress, and lack of sleep.
Pseudomembranous inflammation of the large intestine
This name has an inflammatory process in the colon, developed as a result of dysbiosis. Its symptoms are observed while taking antibiotics and after their withdrawal. They are as follows:
- frequent watery stools, with impurities of mucus and blood;
- abdominal pain, which intensifies with bowel movements;
- a slight increase in temperature;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- weight loss.
Proctitis and sigmoiditis
With inflammation of the lower part of the large intestine, which is isolated most often develops with prolonged use of antibiotics, injuries by foreign bodies, chemical or thermal burns, such signs will be observed:
- pain in the rectum, worse with bowel movements;
- secretion of blood and mucus from the anus;
- constipation
- foreign body sensation in the anus;
- urge to defecate;
- body aches;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the rectum during bowel movements.
Inflammation of the intestinal lymph nodes
If intestinal inflammation had an infectious cause, but in some cases as an independent disease, especially in children, inflammation of the intestinal lymph nodes may develop. These structures serve as a barrier to infection, and when it gets in too much or the microorganisms are too aggressive, the lymph nodes become inflamed. This is manifested as follows:
- acute paroxysmal pains develop in the abdomen, especially in the lower right (as with appendicitis);
- temperature rises;
- nausea and vomiting appear;
- diarrhea or constipation occurs.
Abdominal pain lasts from several hours to three days, do not become more intense. With these symptoms, there is no deterioration in the general condition of a person, which would be with appendicitis or other surgical pathology.
How is the diagnosis
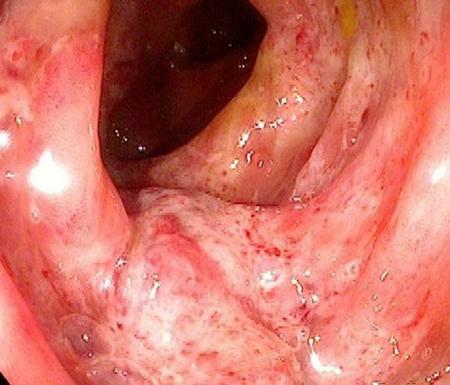
The main method to establish the localization and type of the inflammatory process is endoscopic examination
In order to establish the type, cause, location and nature of intestinal inflammation, such studies are carried out:
- general blood analysis;
- coprogram - analysis of feces;
- bacteriological examination of feces;
- biochemical blood tests;
- endoscopic examination of the intestine: can be carried out only with lesions of the colon. It has the name colonoscopy (if the entire colon is examined) or sigmoidoscopy (if only the rectum and sigmoid colon are examined). During this examination, a biopsy of the desired site may be performed;
- intestinal x-ray with contrast;
- capsular endoscopy is performed to examine the entire intestine, including the small one. It is performed by a person swallowing a capsule equipped with a video camera. She comes out naturally.
If the diagnosis of any of the above diagnoses is confirmed, the question arises of treatment. It is prescribed by a doctor depending on the form and stage of the identified disease and, as a rule, includes a course of medications and a strict diet. But sometimes the patient's condition requires surgical intervention. In general terms, we described the principles of treatment of the pathology considered in the article.