Decompressive laminectomy is a common operation performed along the entire length of the spine from the neck to the lower back (lower back). It is carried out in order to reduce pressure on the roots of the spinal nerves caused by age-related dystrophic changes in the spine (its narrowing), and also to treat other conditions (for example, the consequences of spinal injuries, intervertebral hernias, tumors). Depending on the severity of the disease, one or more vertebrae may be involved. In most cases, the result of the procedure can be removed pain syndromeback to everyday activities.
Spinal cord neuroanatomy
Complete defeat means a complete loss of sensation and muscle control at the lesion site. Almost half of all spinal cord injuries are complete. Most spinal cord injuries, including complete lesions, result from spinal cord injury or loss of blood flow to the bone marrow, not the spinal cord. Complete defeat does not mean that there is no hope of any improvement.
The causes of vertebro-medullary injury are direct and indirect. Direct causes lead to sprains or destruction of the vertebral bodies. Indirect does not affect the structure of the spine, but the energy of the trauma is transmitted to the brain inside the medullary canal. These injuries lead to states of concussion, contraction, contusion, or the medullary region.
Laminectomy is usually used only when more conservative methods of treatment, such as drug therapy, physiotherapy or injections, do not work. The procedure can also be recommended if severe symptoms are observed or the patient's condition worsens sharply.
Why is this operation done?
Bony growths in the spinal canal can narrow the space reserved for the spinal cord and nerves. This pressure causes pain, weakness, or numbness in the arms and legs. In most cases, a laminectomy helps relieve these symptoms.
Concussion: this is manifested in a decrease or temporary loss of function of the medullary segments below the affected area. Medullary contraction: it is characterized by a neurological syndrome in which a medullary disorder is caused by both medullary shock and contraction on the brain. Maduva is not subject to structural effects, is compressed by the flight of bones or combined hematoma. Loss of control over the medullary functions controlled by segments below the injury area is lost. spinal cord injury: in this case, neurological disorders occur with structural damage to the bone marrow during trauma, but it is not disturbed. medullary section: in this situation, the brain is partially or completely divided. There is no structural damage to the bone marrow. . Many of the traumatic lesions of the bone marrow are caused by secondary events from the minutes and hours after the injury.
She is appointed by a neurosurgeon in the following cases:
- severe, gradually worsening symptoms limit the possibilities for normal daily activities;
- conservative treatment methods do not relieve pain and do not reduce symptoms caused by compression of the nerve (numbness, weakness);
- the patient has difficulty controlling the bladder and intestines;
- sudden changes in the ability to take a stable position when walking are noticed, movements become awkward.
In some cases, a laminectomy can become part of a complex of surgical procedures aimed at treating an intervertebral hernia. The surgeon will need to remove part of the bone plate to gain access to the damaged disc.
As a rule, direct lesions that do not have a structural effect on the brain cause small pericapal bleeding, which confuses gray matter. About 4 hours after the injury, infection with gray matter and swelling of the white matter occurs. A heart attack with a lesion occurs within 8 hours after an injury. It is important to know that necrosis and hematoma expand and occupy a segment or two above and below the main affected area. Bone tissue is trying to recover through the process of gliosis, which develops in areas of necrosis several months after the injury and can cause singioomyelia syndrome.
When deciding on the feasibility of the procedure, the neurosurgeon is based not only on the results of imaging (X-ray diagnostics and computed tomography). Even if the tomography shows that the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots are compressed, the recommendation for surgical intervention occurs only if there are severe symptoms that interfere with the ability to conduct normal life activities.
From a functional point of view, spinal cord injury causes medullary shock and supraminal functional inhibition of a sublevel segment. In the situation of the medullary region, there is flaccid paralysis and the abolition of osteotonic reflexes, sensitivity disorders, sphincteric and trophic disorders in the sublingual segments. The brain loses control over the sublevels of the medullary segments. This symptomatology lasts 1-3 weeks, after which the recovery period of cerebral automatism is established.
Osteotonic reflexes become exaggerated, a Babinsky sign appears, and some limb movements can be resumed if the brain has not been completely torn. If the bone marrow had an incomplete or complete incision or a medullary infarction, in the first moments of the injury a patient with lower limbs did not throw out an arbitrary or involuntary movement. The only engine reaction that is sometimes visible in the early days of an injury is the slow movement of the halo flexion after scratching the plant.
What happens before the operation?
- a few days before the operation most likely you will need to undergo an examination (take a blood test, cardiogram, perform an x-ray of the chest).
- the neurosurgeon will offer to sign a consent form and fill out the necessary documents with personal information regarding your medical history (indicate the presence of allergic reactions, including anesthesia, the number and limitation period of the last blood transfusion, describe the medications / vitamins taken, previous operations).
- you may want to donate your own blood a few weeks before the operation in order to be able to use it for transfusion during the operation.
- a week before the operation, stopping the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and blood thinners will be required;
- cessation of smoking, chewing tobacco, drinking alcohol two weeks before and as much after surgery, because they can lead to problems with blood coagulation and cause blood loss.
You should come to the hospital in the morning of the day on which the procedure is scheduled. Water intake stops after midnight before. An intravenous catheter is connected to the patient’s arm for subsequent administration of anesthesia.
The condition described above lasts several days or several weeks, depending on the severity of the lesion, after which an automated brain mechanism appears. During this time, trophic disorders develop, eludes in compressed areas. If the injury seriously affects the bone marrow, an automated brain mechanism occurs after a few weeks.
Bronchial automatism is manifested in the appearance of the Babinsky sign, triple reaction reflexes, and osteotonic reflexes are exaggerated. Maintain sphincter disorders. At this stage, trophic disorders tend to regress. Late contractions occur in the lower extremities, which leads to spastic paraplegia in flexion.
What happens during surgery?
Laminectomy cervical The spine, like the spinal, is carried out in 6 stages. The duration of the procedure is 1-3 hours.
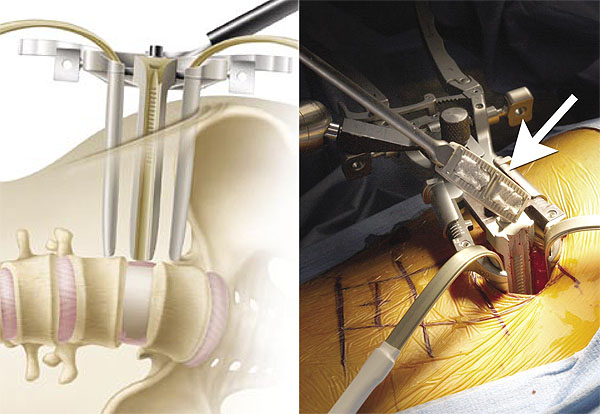
The risks of laminectomy
Potential risks and complications for the described procedure.
| Type of complication | Probability | Description |
| Nerve Root Damage | 1 in 1000 | Paralysis |
| Bowel / Bladder Damage | 1 in 10,000 | Urinary / fecal incontinence |
| Cerebrospinal fluid leak | 1% to 3% | Does not affect the outcome of the operation, with this type of damage, the patient will have to lie still for about 24 hours to make up for the leak |
| Infections | About 1% (as with other types of surgical interventions) | Despite the fact that infection is one of the serious problems, it often requires additional surgical intervention to clean, the use of antibiotics, as a rule, it can be eliminated with high efficiency |
| Blood loss | They happen extremely rarely, because in the operated area there are no large blood vessels | |
| Postoperative instability, the need for further operations | 5-10% | The procedure relieves symptoms, but does not stop the progression of facet joint degeneration. |
The likelihood of common anesthetic complications, such as myocardial infarction (heart attack), blood clots, stroke, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism is about the same as with any other type of surgical intervention.
Clinical manifestations depending on the topography of the lesion. In case of vertebral injury, there are dislocations and fractures of the atlas, body axis, and odontoid apophysis. These elements lead to slipping of the head limb to the front of the head, which leads to depression of the bulb by the odontoid apophysis. In the case of damage to the bulbar, the damage is fatal, which leads to exit through cardiorespiratory arrest. If the flask is not damaged, tetraepilation occurs with anesthesia from C2 and respiratory distress. When the fractures are not structurally interested in the bone marrow or bulb or are of little interest, the patient returns completely neurologically. Some people experience a decrease in muscle strength in their upper limbs. However, after a few months, tetraparet syndrome can sometimes occur due to a local arachnoid process. fracture rate also causes respiratory disorders, affecting the physical nerve. Paralysis occurs at the level of the deltoid and superficial and subpinal muscles. Fractures and lead to paralysis of the biceps. Lesions are caused by triceps, extensors of the forearm and muscles of the forearm. lesions at and below levels lead to paraplegia. There are also sphincter disorders. The most common fractures occur in the area between the vertebrae. Impairment of the lower thoracic spine can lead to congenital or caudal condyle syndrome. fractures occur in the event of an impact in the upper or middle back. Clinically related are signs of horse cone and tail dysfunction. In case of spinal cord injury, a simple radiograph of all segments of the spine is performed.
What are the results?
 Decompressive laminectomy successfully relieves leg pain in 70% of patients, allowing a significant improvement in their function (ability to perform normal daily activities), the level of pain and discomfort is markedly reduced.
Decompressive laminectomy successfully relieves leg pain in 70% of patients, allowing a significant improvement in their function (ability to perform normal daily activities), the level of pain and discomfort is markedly reduced.
However, back pain does not completely disappear, and 17% of patients require another surgery, symptoms may return in a few years.
Treatment begins at the scene of the accident. The neck should be immobilized with a special collar so that the brain will not become even more damaged during the mobilization of the patient, avoiding rotation and stretching of the neck, torsion or torsional rotation. If necessary, the patient is intubated, but maneuver to expand the neck is avoided.
Therefore, it is useful to administer an infusion of crystalline or colloidal solutions. Recent studies have shown that administering high doses of glucocorticoids as quickly as possible due to an accident improves the functional prognosis. The accident should be urgently transferred to the neurosurgery department. During transportation, the patient should be in a supine position, on the dorsal lowering. In a specialized service, treatment follows the resuscitation of the patient, removing him from shock. Fluid loss will be monitored by installing a urine probe and a nasozoic stomach probe.
The results of the operation are largely up to you. It is important to maintain a positive attitude and diligently perform physical exercises, maintain an optimal level of weight suitable for your height. This phoned to reduce the load on the spine and reduce pain. Do not console yourself with vain hopes of hoping that you will be "like new" immediately after the procedure. It is important to understand that back pain will always accompany you, you must learn to take the right postures and techniques to prevent re-injury.
In surgery, in relation to orthopedic or surgical indications, an attempt will be made to reduce the focal point of the fracture. If necessary, a laminectomy is performed with the attachment of osteosynthesis. It is difficult to establish an exact protocol that recommends specific orthopedic or surgical behavior. The experience gained by neurosurgeons puts forward the idea that an immediate surgical indication with a laminectomy causes medullary decompression and enables local assessment of the state of the brain tissue.
Consider the following. Orthopedic treatment is recommended in the case of fractures with little movement or big movement, but without medullary compression, as well as fractures with cervical dislocations. surgery is recommended in case of obvious medullary compressions. He also intervenes surgically in situations of large dislocations with column instability and injuries, which are enhanced by paraplegia during orthopedic treatment. Fractures of the spine should be taken into account in order to detect compression dislocations of the spinal cord to produce instabilities caused by compression fractures that can lead to spinal follow-up detection and proper treatment of fractures of the stems, chamfer or vertebral body.
Read reviews of patients who have been treated abroad. In order to receive information about the possibility of treating your case, leave us a request for treatment at this link.
To avoid urinary tract infections, it is recommended to change the probe daily. Dry skin care from dangers. In addition, in order to avoid cuts and ulcers of the skin, the patient is periodically mobilized, especially in the area of \u200b\u200bcompressed areas. For a general improvement, blood transfusions, vitamin, protein, lipids and carbohydrates in recommended amounts for each person are recommended. When the patient's situation allows, after the fracture is immobilized, the functional rehabilitation of the normal medullary segments will be accompanied by medical gymnastics.
Be sure to consult a doctor before treating diseases. This will help to take into account individual tolerance, confirm the diagnosis, verify the correctness of treatment and eliminate negative drug interactions. If you use prescriptions without consulting a doctor, then this is entirely at your own peril and risk. All information on the site is presented for educational purposes and is not a medical aid. All responsibility for the application rests with you.
This article was written by Daniel Nexulescu, a contributor to the project. The purpose of this study is to determine the clinical and surgical results after lumbar laminectomy. We retrospectively reviewed medical records of neurosurgical patients who underwent first-level lamectomy, bilateral, level 1-3 for a degenerative disease of the lumbar region. Patients with dissectomy, complete facetectomy, and fusion were excluded.
Five hundred patients were observed for an average of 79 months. After lumbar laminectomy, patients showed a statistically significant improvement in back pain, neurogenic claudication, radiculopathy, weakness, and sensory deficiency. The rate of intraoperative durotomy was 00%; however, 60% experienced postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage. The risk of at least one postoperative complication with lumbar laminectomy was 60%. Seventy-two patients needed reoperations to progress a degenerative disease over 40 years.