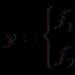Every business entity must be able to calculate the value of net assets.
The assets of an organization are everything that belongs to it (property, investments, obligations of third parties to it), everything that generates profit and that can be converted into cash.
Along with the specified property and investments, the organization, during its existence, always has obligations to third parties. Net assets (also use the prefix “net”, net assets) are all that will remain at the disposal of the company after it pays off all its liabilities. The term “own funds” is used as a synonym in the economic literature and some regulatory sources. At its core, this is what the organization owes to the business owners, founders, in economic terms, the so-called “price of business”, since the owners of the company in the event of its liquidation or bankruptcy can count on paying off debts to them last, after the organization's obligations to other creditors will be repaid.
On the other hand, own funds act as a financial guarantee for the organization’s fulfillment of obligations to third parties. In socially significant activities, the requirements for the amount of equity capital in the relevant area (for example, in banking, insurance) are very high.
This concept has extremely important practical application, and therefore this material is devoted to the study of the algorithm for assessing the value of the net assets of LLCs and JSCs and the analysis of some important cases of application in activities. Hereinafter, in the text of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ will be referred to as “Federal Law No. 14-FZ”, Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated 12/26/1995 N 208-FZ - “Federal Law No. 208-FZ” "
Please note that currently there is a single The procedure for determining the value of net assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2014 N 84n (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure) for various organizational and legal forms legal entities- JSC, LLC, state and municipal unitary enterprises, production cooperatives, housing savings cooperatives, economic partnerships, with the exception of credit organizations and joint-stock investment funds.
Note. The credit institution calculates, in the manner established by the Bank of Russia, the amount of its own funds (capital).
How to calculate net assets
The net asset value is determined as the difference between the value of the organization's assets accepted for calculation and the value of its liabilities accepted for calculation.
Let's figure out what we exclude when performing calculations. First of all, we do not take into account accounting objects recorded on off-balance sheet accounts (for example, leased fixed assets, inventory items accepted for safekeeping, security for obligations and payments).
For the calculation of assets, we do not accept receivables from the founders (participants, shareholders, owners, members) for contributions (contributions) to the authorized capital (authorized fund, mutual fund, share capital), for payment for shares.
When calculating liabilities, we do not accept deferred income recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property.
We take everything else into account when making calculations.
We carry out calculations based on accounting data. For this we need a balance sheet. This follows from clause 7 of the Procedure.
In its most simplified form, the formula for calculating net asset value will look like this:
NA = Assets to be calculated - Liabilities to be calculated
Using the provisions of the Procedure, as well as the structure of the balance sheet, we obtain the following detailed formula:
NA = (Section I + Section II - Management Debt) - (Section IV + Section V - BP Income) = =Section III-MC Debt + BP Income,
where NA is the value of net assets;
Section I* - summary for section. I (non-current assets);
Section II - summary of section. II (current assets);
Section III - summary of section. III (capital and reserves);
Section IV - summary of section. IV (long-term liabilities);
Section V - summary of section. V (current liabilities);
Debt of the management company - debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital;
BP income - deferred income (credit balance of account 98 “Deferred income, subaccounts “Gratuitous receipts”, “State Assistance”).
(*referring to sections of the balance sheet).
JSCs must assess the size of net assets quarterly at the end of each quarter, as well as at the end of the year. LLCs can only make assessments at the end of the calendar year.
Why calculate your net worth?
Reason 1. Exercising financial control over the state of affairs
The indicator is used to monitor the financial condition and reflects the efficiency of the functioning of the business entity.
First of all, the ratio of net assets to the size of the authorized capital (AC) is carried out. Both of these indicators are very important in relation to each other. The value of the latter should be greater. Otherwise, the law requires certain changes to be made within a specified period.
So, the organization’s annual report indicates:
1) the dynamics of changes in both net assets and authorized capital of JSC and LLC for the last three completed financial years, including the reporting year, or, if the organization has existed for less than three years, for each completed financial year;
2) the results of an analysis of the reasons and factors that, in the opinion of the sole executive body of the company, the board of directors, led to the fact that the ratio of indicators was violated;
3) a list of measures that are proposed to be implemented to correct the situation.
A special feature for JSCs: they must make such an assessment of the ratio of indicators quarterly at the end of each quarter. If the net assets turn out to be less than the authorized capital by more than 25 percent at the end of three, six, nine or twelve months of the reporting year following the second or each subsequent reporting year, at the end of which the amount of the authorized capital turned out to be greater, the JSC twice with a frequency of once a month is obliged to place in the media in which data on state registration of legal entities is published, a notice of a decrease in the value of its net assets.
The creditor of the company, if its rights of claim arose before the publication of the specified notice, no later than 30 days from the date of the last publication of such notice, has the right to demand from the JSC early fulfillment of the corresponding obligation, and if it is impossible to fulfill it early, termination of the obligation and compensation for related losses. The statute of limitations for filing this claim in court is six months from the date of the last publication of such notice.
The court has the right to refuse to satisfy such a claim of the creditor if it is proven:
1) the rights of creditors are not violated by such a reduction;
2) the security provided for the proper performance of the relevant obligation is sufficient.
The value of net assets at the end of two financial years in a row cannot be less than the Criminal Code (clause 4 of Article 30 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ, clause 6 of Article 35 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ). Otherwise, no later than six months after the end of the relevant financial year, one of the following decisions must be made:
1) on reducing the authorized capital of the company to an amount not exceeding the value of its net assets;
2) on the liquidation of the company.
The Civil Code also provided an opportunity in this case to take the “reverse” route - to increase net assets to the size of the authorized capital (clause 4 of Article 90 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of Article 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Possible ways of such an increase: making additional contributions to the company's property, using borrowed funds, writing off uncollectible debt, increasing profits and reducing losses, revaluing, issuing shares. Each of these paths has its own difficulties. Usage financial assistance increases the size of liabilities. The increase in profit and revenue is limited by a lack of resources and limited sales markets, etc. You can, on the contrary, take the path of reducing costs and lowering the level of obligations. Such a reduction can be achieved through their restructuring (changing repayment schedules, deferring payments, by paying off part of the debts, which is possible, in turn, if there is a sufficient amount of available funds that can be used to fulfill the organization’s obligations. For these purposes, it is possible, in in particular, to improve work in the collection of receivables, including organizational and judicial work with counterparties, the sale of debts to third parties, offsets, etc.
At the same time, it is worth mentioning the so-called “imaginary assets” - in order to improve performance or for other reasons (technical errors, insufficient qualifications of responsible persons), assets are reflected in the accounting records that should not be reflected there on the date of the assessment. Such “imaginary equity capital” does not bring real profit; it has “value” only on paper. What to hide, sometimes this is done in order to ensure that the organization’s financial performance indicators comply with regulatory requirements (for example, for carrying out activities in licensed areas), to obtain borrowed funds, including credit, for a kind of “adjustment” of tax consequences for the business.
Factors that artificially inflate the value of net assets include, in particular, unrealistic receivables that must be written off (for example, the statute of limitations has expired, the counterparty has ceased to exist without succession), fixed assets unsuitable for use due to wear and tear, or intangible assets unusable due to obsolescence, as well as investments in subsidiaries conducting unprofitable activities, when the value of such a subsidiary due to unprofitability is lower than the amount of investments in it, etc.
Reason 2. Payment of dividends
As stated in paragraph 1 of Article 29 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ, an LLC does not have the right to make a decision on the distribution of its profits if, at the time of making the decision, the size of its net assets is less than its capital and reserve fund or becomes so as a result of such a decision.
Similar restrictions are established by law for JSCs, which do not have the right to make a decision (announce) on the payment of dividends on shares and pay declared dividends if on the day of such a decision / on the day of payment, respectively, the size of the JSC’s net assets is less than its authorized capital and reserve fund , and the liquidation value of the placed preferred shares exceeds the nominal value determined by the charter or becomes less than their size as a result of such a decision/as a result of the payment of dividends (clause 1, 4 of article 43 of the Federal Law No. 208-FZ).
Reason 3. To calculate the actual value of the share
The actual value of the share of an LLC participant corresponds to the part of the value of net assets proportional to the size of his share (Clause 2 of Article 14 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ).
In what cases will it be necessary to calculate it?
Firstly, in the case of the acquisition of a share by the Company at the request of its participant, when the constituent documents prohibit its alienation to third parties, and other participants refused to acquire it, or, in accordance with the charter, it is necessary to obtain consent for alienation, but it was not received.
Secondly, in cases where a company acquires a share at the request of its participant who voted against the general meeting making a decision to carry out a major transaction or to increase the authorized capital, in accordance with clause 1 of Art. 19 Federal Law No. 14-FZ, or who did not take part in the vote.
In the two indicated cases, the period for payment is three months from the date of occurrence of the corresponding obligation, unless otherwise specified in the charter. Its size is determined on the basis of the company’s financial statements for the last reporting period preceding the day the corresponding request was submitted.
Thirdly, in cases of exclusion of a participant, when his share has passed to the LLC.
Fourthly, when the consent of the LLC participants has not been received to transfer the share to the heirs, legal successors, the buyer at a public auction, the founders (participants) of a liquidated legal entity who have proprietary rights to its property or rights of obligations in relation to this legal entity.
Fifthly, in the event of a participant leaving the company (if the Charter does not contain a corresponding prohibition) by alienating his share of the LLC.
Sixthly, in the case when the LLC pays the creditors of its participant the actual value of its share at the request of the creditors.
The payment is made from the difference between the value of the company's net assets and the size of its capital. If such a difference is not enough, the obligation to reduce the authorized capital by the missing amount is prescribed.
Reason 4. Increase in authorized capital
An LLC may increase its authorized capital at the expense of its property, and (or) at the expense of additional contributions of its participants, and (or), if this is not prohibited by its charter, at the expense of contributions from third parties accepted into the company.
If the increase occurs at the expense of property owned by him, one cannot do without calculating the amount of net assets, since clause 2 of Art. 18 Federal Law 14-FZ establishes the rule: the amount by which the authorized capital is increased at the expense of the property owned by it should not exceed the difference between the net assets of the LLC and the amount of the authorized capital and its reserve fund.
A JSC can increase its authorized capital by increasing the par value of shares or placing additional shares. At the same time, an increase by placing additional shares can be carried out at the expense of its property, and if it is through an increase in the nominal value of the shares, then it is carried out only at the expense of the JSC’s property.
For cases of increasing the authorized capital of a JSC at the expense of its property, a rule similar to the rules for an LLC has been established: The amount by which the authorized capital is increased joint stock company at the expense of the property of the joint-stock company, should not exceed the difference between the size of net assets and the amount of the authorized capital and its reserve fund (clause 5 of Article 28 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ).
Reason 5. Reduction of authorized capital.
Federal Law No. 208-FZ establishes for a JSC the possibility of reducing the authorized capital, and also establishes cases of its mandatory reduction. In this case, you also cannot do without the calculations that our article is devoted to.
Firstly, in this case the rule must be observed: the ratio of the amount by which the charter capital is reduced to its size before the reduction cannot be less than the ratio of the funds received by shareholders and (or) the total value of the equity securities purchased by them to the size of net assets, the cost which is determined according to its accounting data as of the reporting date for the last quarter preceding the quarter during which the board of directors (supervisory board) made a decision to convene a general meeting of shareholders, the agenda of which contains the issue of reducing the authorized capital (clause 3 of article 29 of the Federal Law 208-FZ).
Secondly, the law prohibits a JSC from making a decision to reduce if, on the day of its adoption, the size of its net assets is less than the sum of its authorized capital, reserve fund and the excess of the liquidation value of the issued preferred shares over the nominal value determined by the charter or becomes such as a result of actions carried out in accordance with the rules of paragraph 3 of Art. 29 Federal Law No. 208-FZ payment of funds and (or) alienation of issue-grade securities.
As you can see, the calculation of net assets is extremely important in the life of every business entity. Its indicators give the company reliability, strengthening its credibility in the market, expand its ability to attract financial resources, and strengthen confidence in solvency and sustainability.
Using the calculation skills discussed in this article, an enterprise can promptly respond to changing conditions, monitor negative trends, and flexibly overcome them. Management decisions can be made under conditions of complete, objective and comprehensive information about the value of net assets and its dynamics. The duty of a joint-stock company to provide any interested party with access to information about the amount of its net assets is established by law. As we know, LLC participants have the right to receive any information about the activities of the company, including indicators of the value of net assets. errors in the alienation of a share in the authorized capital of the company; litigation;
4) ;
5) ;
6) .
To timely ensure the adequacy of equity capital and control over the proper fulfillment of obligations, the legislation provides for the determination of the value of net assets.
Net assets - These are assets secured by the organization's own capital. In other words, this is the book value of the assets that would remain at the disposal of the participants of a commercial organization if it were to pay off all its obligations.
In general, the value of net assets is calculated by organizations (with the exception of insurance organizations and legal entities engaged in professional and exchange activities in securities) once a year - on January 1. The legislation may establish a different frequency<*> .
When determining the amount of net assets, balance sheet data is used<*> .
Net asset value is determined as the difference between the value of assets and liabilities taken into account<*> .
The assets accepted for calculation include <*> :
- long-term assets (section I of the balance sheet): fixed assets, intangible assets, profitable investments in tangible assets, investments in long-term assets (including equipment for installation and construction materials), long-term financial investments, deferred tax assets, long-term receivables, other long-term assets;
- short-term assets (section II of the balance sheet): inventories, long-term assets intended for sale, deferred expenses, value added tax on purchased goods, works, services, short-term receivables, short-term financial investments, cash and cash equivalents, other short-term assets.
The liabilities accepted for settlement include <*> :
— long-term liabilities (section IV of the balance sheet): long-term loans and borrowings (excluding interest on them), long-term obligations for lease payments, deferred tax liabilities, deferred income, reserves for future payments, other long-term liabilities;
— short-term liabilities (section V of the balance sheet): short-term loans and borrowings (except for interest on them), short-term part of long-term liabilities, short-term accounts payable (including interest on loans and borrowings), liabilities intended for sale, deferred income, reserves for future payments, other short-term liabilities.
The calculation formula can be schematically presented as follows:
Calculation of net asset value is completed in the form in accordance with Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 35 dated June 11, 2012. The calculation provides not only the final indicators of the balance sheet sections on lines 190, 290, 590, 690, but also their components.
Example. The value of net assets as of January 1, 2017 amounted to 14,905 thousand rubles. Let's calculate the net asset value as of January 1, 2018.
Initial data from the balance sheet:
Long-term assets (line 190 of the balance sheet) – 53,350 thousand rubles.
Short-term assets (line 290 of the balance sheet) – 337,301 thousand rubles.
Long-term liabilities (line 590 of the balance sheet) – 70,329 thousand rubles.
Short-term liabilities (line 690 of the balance sheet) – 234,959 thousand rubles.
Net asset value atJanuary 1, 2018 will be 85,363 thousand rubles. (53350 + 337301 –70329 – 234959).
The value of the organization's net assets for 2017 increased significantly compared to 2016 (RUB 85,363 thousand ˃ RUB 14,905 thousand). The organization's level of equity capital is high.
Note that since the assets and liabilities taken into account correspond to the results of the balance sheet sections, the value of net assets will be equal to the value of equity capital (the total of section III of the balance sheet).
It should be noted that if at the end of the second and each subsequent financial year the value of the net assets of a commercial organization is less than the authorized capital, such an organization is obliged to reduce its authorized capital in accordance with the established procedure to an amount not exceeding the value of its net assets.
If the value of the net assets of a commercial organization for which the minimum size of the authorized capital is established by law, based on the results of the second and each subsequent financial year, decreases below the minimum size of the authorized capital, such organization is subject to liquidation in the prescribed manner<*> .
Net assets are one of the most important financial indicators. For their correct analysis, correct calculation is required.
The concept of net assets
Each company has property, which includes real estate, land, and money. These are assets. Also, every commercial structure has obligations and debts to counterparties. Net assets are a company's property and cash minus its liabilities. They are calculated once a year. The results are required to be reported in annual reports.
The calculation procedure is established by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2014 No. 84. It is relevant for a number of structures:
- State unitary structures.
- Production.
- Housing cooperatives.
- Economic associations.
The calculation must be performed strictly according to established standards. Special formulas that are approved by the state are used.
Why are calculation results needed?
The amount of assets must be calculated once a year. This is necessary for the following purposes:
- Control over the financial condition of the structure. The result of the calculations allows us to understand the efficiency of the structure. The size of the NAV is compared with the volume of the authorized capital. If the NAV is greater than the authorized capital, this indicates the normal position of the company. If the capital exceeds the amount of capital, then measures must be taken immediately to correct the situation. If this ratio does not change over the course of two years, the entrepreneur must either reduce the authorized capital or liquidate the organization.
- Dividend payment. According to Article 29 of the Federal Law No. 14 dated 02/08/1998, dividends can be distributed only after an analysis of the economic condition of the company. In particular, it is necessary to identify the ratio of MC and NA. If the latter value is less than the authorized capital, dividends cannot be paid.
- Determining the real value of a share. The real value of the LLC founder's share is the volume of net assets corresponding to the size of the share in question. This definition is specified in paragraph 2 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14.
- Increase in capital. The capital can be increased at the expense of either the organization’s personal property, or additional contributions from participants, or funds from third parties, if permitted by the Charter. The increase can only be carried out by the amount of the difference between the NA and the size of the authorized capital.
- Reducing the Criminal Code. Sometimes the Criminal Code must be reduced without fail. The decision to reduce capital is made based on the volume of net assets and their ratio to the capital.
Almost every organization is faced with the need to determine the size of its net assets.
In what cases is the calculation made?
NA must be calculated in the following cases:
- Purchase by an LLC of a participant’s share at his request in the event that the share cannot be acquired by third parties according to the Charter.
- The company’s purchase of the share of a participant who voted at a meeting against the implementation of a major transaction or change in the size of the authorized capital.
- Exclusion of a participant from the company with the subsequent transfer of his share to the LLC.
- The participant is required to pay creditors with his share.
- It is required to determine the financial condition of the company.
- A decision is made to pay dividends.
- Reduction or increase of capital.
Asset size– this is the most important indicator for any business entity. Regular calculation of the parameter under consideration provides a number of advantages for the company: reliability, strengthening market positions, increasing opportunities to attract resources, sustainability. Open data on private equity is the confidence of counterparties in the solvency of the organization.
Formula for calculating the indicator
To calculate, you need to find the difference between assets and liabilities. That is, the difference between the company’s property and existing obligations is determined. The assets combine:
- Real estate owned by the structure.
- Land.
- Income from activities.
- Various property, including equipment, tools, furniture, office equipment.
The assets do not include receivables of the founders for contributions to the management company. Liabilities are the company’s debts: short-term and long-term liabilities, various loans, collections. They do not include income from subsequent periods received in connection with state assistance or gratuitous acquisition of property.
So, the following formula is used for calculation:
(line 1600 – charger) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP)
The formula uses the following definitions:
- ZU – debt of the founders for contributions to the management company.
- DBP – income of the following periods in the form of government assistance or gratuitous acquisition of property.
All relevant lines are taken from the balance sheet.
Analysis of calculation results
There are three net asset values obtained as a result of calculations:
- Negative. Indicates the predominance of liabilities over income. That is, the company's activities are not commercially successful. The organization is completely financially dependent on creditors. She has no own funds.
- Positive. Indicates a positive increase in funds. That is, the company fully covers all its debts and also has its own funds.
- Zero. Indicates that the company is breaking even, but does not bring any profit.
Negative calculation results indicate a high risk of bankruptcy of the organization.
Calculation example
Let's look at an example. The balance sheet of the construction company "Reliability" contains the following values:
- discussed in the first section: the residual value of fixed assets is 2.3 million rubles, the capital contribution to unfinished construction projects is 1.6 million rubles, long-term deposits are 700 thousand rubles.
- specified in the second section: the organization’s reserves amount to 200 thousand rubles, debt to debtors – 800 thousand rubles, debt of the founders for contributions to the management company – 50 thousand rubles, cash – 1.2 million rubles.
- Capital of the company specified in section 3: The capital is 200 thousand rubles, retained earnings are 1.5 million rubles.
- Long-term debts discussed in section 4 in the amount of a million.
- Short-term debts specified in section 5: short-term debt in the amount of 400 thousand rubles, debt to the budget - 200 thousand rubles, other debts - 1.9 million rubles.
When performing calculations, the debt to the founders for contributions to the management company is not taken into account. In the case under consideration, it is 50 thousand rubles. The following calculations are carried out:
2,300,000 – 1,600,000 + 700,000 + 200,000 + 800,000 – 50,000 + 1,200,000 = 6,750,000 rubles
From this indicator you need to subtract the indicators of the third section of the balance sheet. The following calculations are performed:
1,000,000 + 400,000 + 200,000 + 1,900,000 = 3,250,000 rubles
The size of assets in this case is 3,250,000 rubles. This is a positive value. That is, the construction company is functioning quite successfully. Its profits exceed its debts. The organization brings money to its founders. As a rule, this NA value is considered in relation to other indicators. Usually this is the authorized capital.
The calculation of net assets on the balance sheet is carried out in accordance with the requirements of Order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. The procedure must be applied by JSCs, LLCs, municipal/state unitary enterprises, cooperatives (industrial and housing) and business partnerships. Let us consider in detail what the term net assets means, what significance this indicator has for assessing the financial condition of a company and what algorithm is used to calculate it.
What determines the size of net assets on the balance sheet
Net assets (NA) include those funds that will remain in the ownership of the enterprise after the repayment of all current liabilities. Defined as the difference between the value of assets (inventory, intangible assets, cash and investments, etc.) and debts (to counterparties, personnel, budget and extra-budgetary funds, banks, etc.) with the necessary adjustments applied.
The calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet is carried out based on the results of the reporting period (calendar year) in order to obtain reliable information about the financial condition of the company, analyze and plan further operating principles, pay dividends received or actually evaluate the business in connection with a partial/full sale.
When determination of net assets is required:
- When filling out annual reports.
- When a participant leaves the company.
- At the request of interested parties - creditors, investors, owners.
- In case of increasing the amount of the authorized capital due to property contributions.
- When issuing dividends.
Conclusion - NAV is the net assets of the company, formed from its own capital and not burdened with any obligations.
Net assets - formula
To determine the indicator, the calculation includes assets, except for the receivables of the participants/founders of the organization, and liabilities from the liabilities section, with the exception of those deferred income that arose due to the receipt of government assistance or donated property.
General calculation formula:
NA = (Non-current assets + Current assets – Debt of the founders – Debt of shareholders in connection with the repurchase of shares) – (Long-term liabilities + Short-term liabilities – Income attributable to future periods)
NA = (line 1600 – ZU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP)
Note! The value of net assets (the formula for the balance sheet is given above) requires, when calculating, to exclude objects accepted for off-balance sheet accounting in the accounts of secondary storage, BSO, reserve funds, etc.
Net assets - calculation formula for the 2016 balance sheet
The calculation must be drawn up in an understandable form using a self-developed form, which is approved by the manager. It is allowed to use the previously valid document for determining the NA (Order No. 10n of the Ministry of Finance). This form contains all required lines to be filled out.
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet - shortened formula
The value of net assets on the balance sheet - the 2016 formula can be determined by another, new method, which is contained in Order No. 84n:
NA = Capital/reserves (line 1300) + DBP (line 1530) – Debts of the founders
Analysis and control
The size of Net Assets (NA) is one of the main economic and investment indicators of the performance of any enterprise. The success, stability and reliability of a business is characterized by positive values. A negative value shows the unprofitability of the company, possible insolvency in the near future, and probable risks of bankruptcy.
Based on the results of settlement actions, the value of net assets is estimated over time, which should not be less than the amount of the authorized capital (AC) of the company. If the reduction does occur, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the enterprise is obliged to reduce its capital and officially register the changes made in the Unified Register (Law No. 14-FZ, Article 20, paragraph 3). The exception is newly created organizations operating for the first year. If the size of net assets is less than the size of the capital, the enterprise may be forcibly liquidated by decision of the Federal Tax Service.
Additionally, there is a relationship between the value of the NAV and the payment of required dividends to participants/shareholders. If, after accrual of income/dividends, the value of net assets decreases to a critical level, it is necessary to reduce the amount of accruals to the founders or completely cancel the operation until the normatively designated ratios are achieved. You can increase the NAV by revaluing the property resources of the enterprise (PBU 6/01), receiving property assistance from the founders of the company, taking an inventory of obligations regarding the statute of limitations and other practical methods.
Net asset value on balance sheet – line
The organization's financial statements contain all the indicators required for mathematical calculations, expressed in monetary terms. In this case, data is taken at the end of the reporting period. When it is necessary to determine the value for another date, interim reports should be prepared at the end of the quarter/month or half-year.
Attention! The amount of net assets is also displayed on page 3600 of Form 3 (Statement of Changes in Capital). If a negative value is obtained, the indicator is enclosed in parentheses.
To assess the financial position of an enterprise in a particular period, it is worth carefully studying the balance sheet as of the reporting date. It is there that the main digital indicators of its activities are indicated. To correctly calculate all standards, special formulas have been created.
Calculations require special accuracy in order to correctly determine the state of affairs at the enterprise.
The essence of the concept of net assets
One of the most important indicators is the size of net assets (hereinafter referred to as NAV).
The reason for this is that it is this indicator that shows the size of the enterprise’s property, from which all obligations that it has to the partners of its activities have already been deducted.
This litmus test of a company’s financial independence is regulated by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, as well as the Federal Commission, which controls the operation of the Central Bank market. Their instructions were developed for LLCs, but due to the fact that this concept is not separately allocated for other types of organizations in the regulatory act, therefore the Decree applies to other organizational forms of conducting economic activities of companies.
Net assets are considered the most effective indicator of the company's condition on the date this indicator is determined.
It is by their size that they are assessed:
- the financial health of the organization;
- effectiveness of the company's chosen strategy;
- financial viability of the company;
- the cost of shares of business participants.
NAV is considered one of the most important indicators, both on the balance sheet and in the company’s activities as a whole. Therefore, maximum attention must be paid to their determination and maintenance at a decent level.
What is included in the structure of the HA
In its simplest sense, this indicator indicates the size of the company’s owners’ net worth. That is, this is what will remain with them after paying all their debts to partners, government agencies and other persons to whom the company owes.
In other words, we can express the essence of this concept as the difference between the figure of absolutely all the assets of the enterprise, as well as its liabilities. It is these indicators that make up the structure of this indicator.
All assets are compiled from certain lines of one of the most important accounting documents, the balance sheet:
- a group consisting of elements of non-current property of an enterprise;
- assets that are in circulation during the main activity of the company.
The first group is data from the first part of the balance sheet.
This includes:
- property of an intangible nature;
- fixed assets;
- construction work that has not yet been completed;
- investments in material assets, which are investments with the aim of obtaining maximum income;
- investments for a long period.
The second group of structural elements for calculating this indicator should be found in the next part of the main reporting document of accountants.
Financiers classify the following data on the company’s activities as assets in circulation:
- inventories, as well as VAT on acquired property, debtor obligations;
- short-term investments;
- monetary resources, as well as other funds in circulation.
The structure of the private equity does not include real expenses that occurred during the repurchase of shares into one’s own possession for planned resale or destruction. In addition, the share funds of shareholders that have not been contributed to the authorized capital should not be classified as current assets.
Liabilities that reduce net assets include:
- amounts of debt on short-term loans;
- amounts required to repay long-term loans;
- accounts payable;
- unpaid profits of investors and shareholders;
- reserve amounts of income;
- other obligations received for a short period of time.
The components can be any other indicators that inherently relate to the company's resources or its obligations to creditors.
The calculation of net assets can be found in the video.
Where to look for data to calculate NAV
Net assets are the book value of the company's owners' property that would remain with them if they repaid all of their debts to creditors. Each of the indicators necessary to calculate this figure must be looked for in the balance sheet for the current period, which is taken for calculation.
Attention should be paid to both sections of this financial document. Almost all indicators of each section must be taken into account in the calculations.
The exception is the amounts contributed by the founders to replenish the authorized capital, since these indicators are already taken into account in other lines of the balance sheet. In addition, the amount of the authorized capital itself and profits, which are still classified as undistributed, are not taken into account.
They are displayed in section No. 3 entitled “Capital and Reserves”.
All other indicators must be taken into account when calculating the net assets of the enterprise. That is, to determine this amount, all information can be obtained from the balance sheet.
The size of the NA is calculated at the beginning and at the end of the year. It is indicated in the lines about changes in capital of financial form No. 3 by all organizations, regardless of the form of business organization.
Calculation of net assets on the balance sheet: determination formula
To find out the size of the NA, it is necessary to carry out a calculation using a formula that is obtained from the very concept of this term.
But, based on the balance sheet data, it will have a slightly more specific form, namely:
NA = STRb 1600 (or STRb 1100+1200) – non-payment of founders (STRb 1400 + STRb 1500),

In addition to balance sheet indicators, you can also take into account accounting data. The essence of this calculation is to carry out the calculation using the amounts that are listed in certain accounting accounts.
In this case, the formula will look like this:
NA = STRb 1300 – debit account balance 75 + account credit balance 98,
- line 1300 of the balance sheet is capital and reserves;
- the debit balance of account 75 is the amount of debt of participants on contributions to the authorized capital, and the credit balance of account 98 is deferred income.
Correct calculation of NA using an example
To calculate net assets, it is necessary to evaluate one of the cases using an example.
| Assets | Amount, rub. |
|---|---|
| 1. Non-negotiable: | |
| — residual value of fixed assets | 1,000 thousand |
| — capital investments in unfinished construction | 500 thousand |
| — long-term investment | 300 thousand |
| 2. Negotiable: | |
| - reserves | 100 thousand |
| - accounts receivable | 400 thousand |
| incl. Unpaid amounts by the founders for replenishment of the management company | 50 thousand |
| Liability balance | |
| 3. Capital and reserves | |
| — UK | 100 thousand |
| — Retained income | 900 thousand |
| 4. Long-term debt: | |
| - long-term loans | 500 thousand |
| 5. Loans for a short period: | |
| — short-term loans | 200 thousand |
| - debt to the budget | 100 thousand |
| — other short-term liabilities | 800 thousand |
In this option, the calculation will be carried out as follows:
А-в = 1000 thousand + 500 thousand + 300 thousand + 100 thousand + 400 thousand = 2,300 thousand (rubles)
As we can see, the amount of 50 thousand rubles was not taken into account, since the unpaid amounts of the founders for the authorized capital are not taken into account.
P-v = 500 thousand + 200 thousand + 100 thousand + 800 thousand = 1600 thousand (rubles).
In liabilities, capital and reserves indicators are not taken into account.
That is, the net asset indicator on the balance sheet of an enterprise with the specified data will be equal to:
NA = 2300 thousand - 1600 thousand = 700 thousand (rubles).
Quite a good indicator of the company's financial performance.
Other methods for calculating net assets
But these calculations are a formula developed by the Ministry of Finance.
Practicing accountants have a slightly different approach to calculation, which involves a slightly adapted scheme for determining the size of net assets:
Net assets = (STRB1600 – account75) – (STRB1400+STRB1400-STRB1530).
This formula does not at all exclude the one developed by the Ministry of Finance; on the contrary, it even more fully reflects the recommendations of the Decrees of this state structure for calculating net assets.
Why are NAs negative?
An indicator is considered negative when the size of net assets is negative. This condition indicates that the company owes more than it owes.
If she has to repay all the debts at once, she will remain bankrupt.
In companies where a minus NA has arisen, the term insufficient property is used to describe the condition. It indicates that the enterprise is obliged to reduce the parameter of its authorized capital or stop operations.
According to Article 20 of the LLC Law, if an enterprise’s net assets as of a specific date are less than those established by the Federal Laws on the registration and activities of enterprises, then liquidation is assumed.
A negative balance of net assets indicates the financial dependence of the business on their creditors, as well as loans.
Why is it important to control cha?
It is net assets, that is, their size, that are very informative in the process of determining the performance of a company. Their size determines the financial viability and independence of the company.
If the company plans to continue its activities, then the NAV must have a positive indicator.
In addition, the success of the company requires their excess above the level of the authorized capital.
This will indicate that the company was able not to waste the initial contributions, but even increased them. This will be ensured by the company’s effective activities in the chosen direction, which will be aimed at maximizing the satisfaction of the interests of customers, which will lead to the sale of its goods and services.
Learn about the method of calculating net assets from the video.
In contact with