The main physical load in the body falls on the hip joint, since it is the support that is most placed on it during walking, running, jumping, etc. Unfortunately, this joint is very susceptible to various diseases, as a result of which a person may completely lose the ability to move normally.
When to perform hip arthroplasty surgery?
The consequences of childhood diseases. Fractures and consequences of hip fractures. It is worth remembering that the better the results of the operation, the synthetic implants of the prosthesis will never be better than the natural hips. Therefore, arthroplasty surgery should be very well indicated and, as a rule, refers to the latest treatment options for hip diseases. Other less invasive and hip-preserving surgeries, such as arthroscopy, have shown good results in some diseases and in many cases are considered the first treatment option.
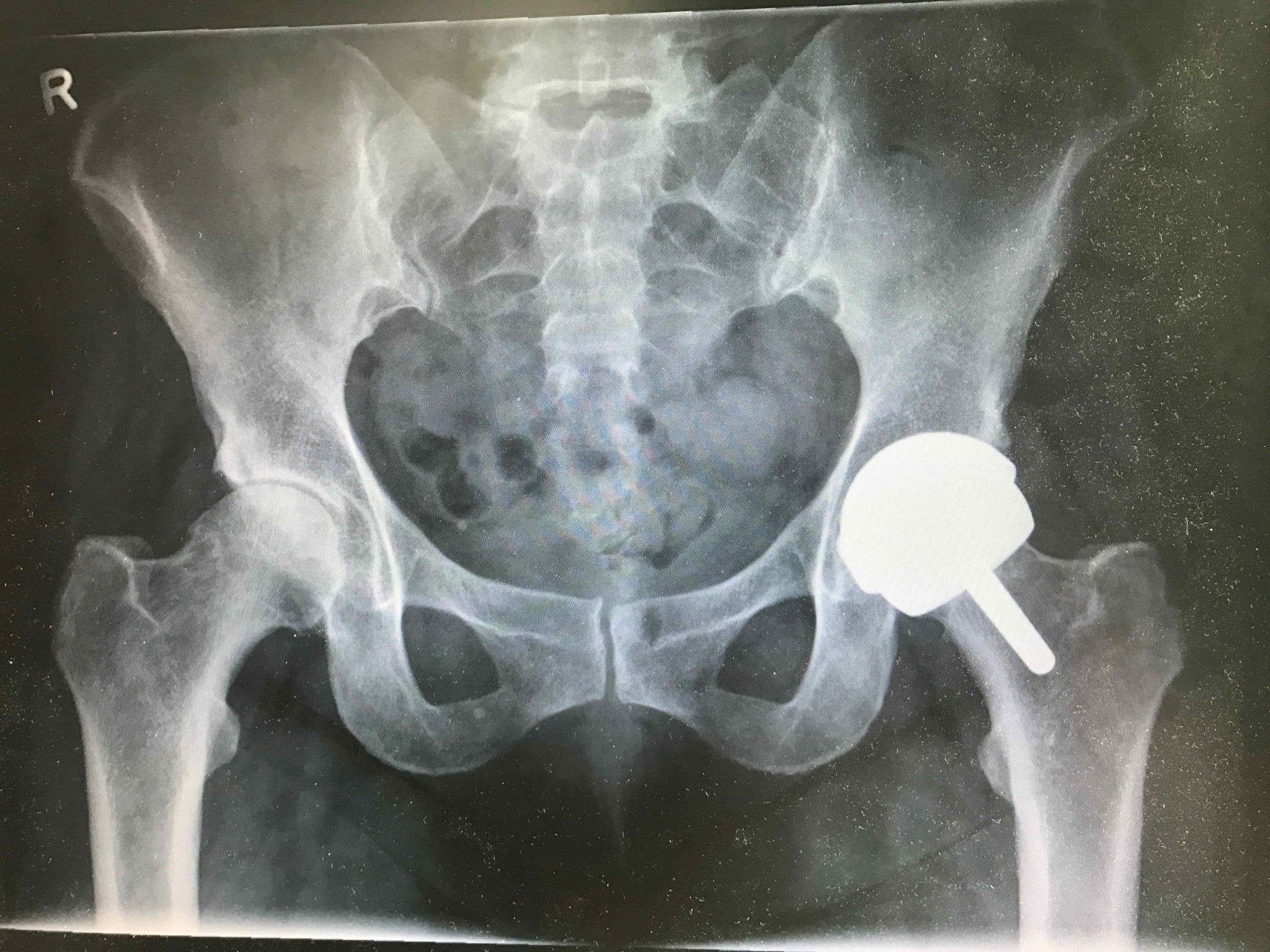
The right TBS (in the left picture) is essentially destroyed, the joint space is completely absent, compare with the joint in the left part of the picture. The diagnosis is coxarthrosis 3-4 degree.
In case of severe damage hip joint surgeons carry out its replacement. The essence of this operation is to replace the affected joint with a disease or trauma, an artificial analogue. Thanks to this, it is possible to completely resume the physical activity of a person, the mobility of his joint, as well as eliminate painful sensations.
Thus, general arthroplasty of the hip joint is indicated in cases of rejection of more conservative or minimally invasive methods of treatment. When it comes to surgery, some criteria are considered. It is known that the later the operation is performed, the lower the chances of the second or third operation to replace the prosthesis, which is a more complex procedure. On the other hand, it is also known that very weakened patients with a high degree of functional impairment also do not respond and have a lower recovery rate than those who previously underwent surgery.
It should be noted that the artificial endoprosthesis has an almost identical structure with natural bone tissues. If successfully installed, such devices can last for decades.

Comparative image of different types of friction pairs of endoprostheses. From left to right: ceramic (black) -polyethylene, metal-metal, ceramic-polyethylene, ceramic-ceramic, ceramic-polyethylene.
Over the past 20 years, there has been a significant evolution of materials used in arthroplastics, especially with regard to wear resistance. But there is not only one factor that contributes to the good evolution of the patient. Choosing a suitable prosthesis, a good sign of surgery and a good placement of implants are some of the factors that affect the results of supporting arthroplasty for a long time.
What types of prosthetics are there?
In addition, the age, size and level of physical activity of patients are factors that cannot be ignored when choosing a prosthesis. It consists of an artificial structure with an anatomical and functional composition similar to a true joint. As in a normal joint, a complete hip prosthesis is formed by two main components: the femoral component and the acetabular component.
In order to better understand the effectiveness of hip replacement, we give the feedback of those patients who have already undergone such an operation:
To have an idea of \u200b\u200bhow the surgery of a given joint goes and what such an operation is in general, you can watch a video of surgeons.
Currently, there are many types of hip prostheses, and they can vary depending on the size, model, type of material, and bone binding medium. In order to function properly, the components of the prosthesis must be well fixed in the bones of the pelvis and femur, and this is mainly guaranteed in two ways: Fixing with cement and fixing without cement. The first method involves the use of orthopedic cement, which functions as a solution that occupies the space between the bone and the implant and thereby promotes fixation between them.
Also, more feedback on the results and possible consequences can be found on the numerous patient forums.
Important! To date, joint replacement surgery is one of the most successful. At the same time, thanks to modern techniques, surgeons can replace both part of the joint (its head), and completely the entire affected joint.
Cement and cementless endoprosthetics
The second method does not use cement, and fixation is provided due to the growth of the patient’s bone in the pores on the surface of the implants. After conducting several preoperative examinations, the surgeon uses the patient’s x-ray to plan the operation using some transparency methods or more recently using computer programs in an attempt to prepare for the patient’s potential difficulties. procedures and evaluate the size of the components used.
In general, after anesthesia, the main stages of the operation are. Incision: An incision is made on the skin, the exact location and size of which depends on a number of factors, including the body conditions of each patient. Three surgical incisions are most often used for hip prostheses: posterior; side or front. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and because of this, with the exception of some cases requiring a specific approach, they say that the best method is the one with which the surgeon is more accustomed.
The total operation involves the replacement of the entire hip joint, as well as its deformed cartilaginous tissues, which, as a rule, are observed in degenerative diseases in humans (arthrosis, coxarthrosis). At the same time, it is the total type of prosthetics that is considered the most effective and durable.
Bone preparation: initially the joint is “deployed”. The femoral head is removed along with the wearing cartilage, and the femoral canal is crushed to obtain a prosthesis stock. The acetabulum scrapers are also carried out with the removal of the remnants of the damaged cartilage, creating a cavity for the acetabular part of the prosthesis.
Prosthetics: The femoral trunk is located in the femoral canal and is attached to the bone under pressure or orthopedic cement, and the head of the femur moves. The acetabulum implant is attached to the bone. Finally, the “new joint” moves, and the surgeon checks and moves the hip. After making sure everything is in order, the soft tissue plans are closed.
According to doctors, this surgery can be performed at almost any age, however, with increased caution, surgery is practiced for elderly patients.

Can prostheses be wiped with hips?
The thigh is the joint through which the stresses pass during everyday life. As soon as arthroplasty is performed, the prosthesis becomes susceptible to these loads and friction, just as the hip joint had already been transferred before surgery. At the same time, over time, the prosthesis tends to wear out, regardless of the material that is made.
Who needs TBS endoprosthetics
Modern prostheses are made with a duration of many years, but some factors interfere with their durability. Among these factors, overweight and a high level of activity performed by the patient stand out. It is important to pay attention to the type of exercise. The patient can and should perform physical exercises, but in this case he must choose actions that have a low effect, such as swimming, walking and water aerobics.
Old age in itself does not mean anything, the main thing is the general condition of the body and, accordingly, the prospects for recovery.
This is justified by the fact that at 70 or at 80, the human body is very weakened and more prone to various complications. Moreover, the regeneration processes in the elderly are slowed down, so that their rehabilitation period can take much longer.
It is important, if necessary, postoperative medical care. In these follow-ups, physical examinations and control radiographs will be performed, which, if associated with any report of abnormal symptoms, can help the doctor perform another hip operation, called an audit.
Physiotherapy in the arthroplasty of the hip joint
Depreciation is one of the common causes of hip failure in the long run and, depending on the condition of the prosthesis, it may be necessary to carry out a revision surgery over time to completely or partially replace the prosthesis.
Preoperative hip arthroplasty
The ideal recovery process begins before surgery. During this period, the patient can begin the rehabilitation process, which includes painkillers and some exercises aimed at improving the patient’s clinical condition and preparing him / her not in order to present severe muscle loss and complications in other joints after surgery.Despite this, there are already more than a dozen cases when elderly patients undergoing a hip fracture underwent total prosthetics, and the procedure was successful, without any serious complications.

These are varieties of a femoral fracture, now they are all successfully treated with surgery to replace the joint.
During the preoperative period, important instructions are also given to explain to the patient the goals of the surgery, the stages of rehabilitation, and especially the care and precautions that the patient should take to avoid postoperative complications, such as dislocation of the prosthesis or venous thrombosis.
Postoperative Hip Arthroplasty
With advances in surgical methods, the patient’s hospitalization period is already relatively short, and recovery itself is more accelerated. Shortly after the operation, and still in the hospital, the physiotherapist urges the patient to sit down and take a few steps, using crutches or walkers, so as not to overload the work area.
When highlighting the main pros and cons of replacing the hip joint, one should indicate its advantages:
- elimination of pain;
- getting rid of edema and the inflammatory process;
- improving the overall quality of life of a sick person;
- relief of the disease and its progression;
- prevention of complications that could occur without surgery (further damage to the bone tissue, inflammation of the knee joint, etc.);
- restoration of normal physical activity.
In addition, thanks to modern new techniques, patients have the opportunity to install endoprostheses from different materials. Also, based on a specific diagnosis, doctors can choose for a person exactly the option of prosthetics that is most suitable for him.
Some of the main problems after this operation are complications such as thrombosis and dislocation. Because of this, in addition to the use of drugs, it is indicated that the patient is performing a contraction of the lower leg muscles, trying to stimulate venous return. It is also important that the patient lies flat on his stomach while lying down, opening his legs slightly and usually with a device called the “abduction triangle” to avoid movements that may cause the prosthesis to dislocate, such as excessive flexion and adduction.
Some hip mobilization exercises and muscle revitalization exercises knee joint, the ankle and hips are performed gradually, but this does not detract from the surgery, since the soft tissues still heal. At this stage, depending on the patient’s condition, the physiotherapist also trains simpler, but necessary tasks for everyday life, such as sitting and standing up and moving up and down stairs.
Despite this, like any open surgical intervention, the replacement has such “against” its implementation:
- High risk of complications.
- Soreness of the procedure.
- A long and rather difficult recovery period.
- The need for anesthesia.
- The risk of infection.
- The need for taking analgesic drugs.
Also, after such a procedure, the patient will need to walk with crutches, but fortunately this measure is temporary, so that with successful rehabilitation, a person may well learn how to move around without accessories.
The first six weeks are an important period for patient adjustment. For this, in addition to training during physical therapy, the house must be adapted to new conditions. One of the first measures is the height of the toilet and the beds and chairs, which can be very low. In addition, throughout this period, and when the incision of the operation is healed, the patient may fall asleep on the side, but when he is lying on the ill-considered side, it is very important that you sleep with a separator between your legs, as a pillow or pillow.
At this time, it is also important to follow the recommendations on how much weight the patient should put on his side, operated during a walk. Progression of the load and time to exit the crutches will depend on factors such as the type of prosthesis, if a graft is used, if there was any fracture at the time of placement of the prosthesis, as well as the quality of the patient’s bone, and this should always be discussed with an orthopedist and physiotherapist.
Types of replacement TBS
Total look
This operation involves the complete replacement of the neck and head of the joint with an artificial analog. This is the classic and most reliable option for prosthetics, which surgeons prefer in most cases.
With successful total prosthetics, the implant is able to serve a person from 15 to 30 years old, which is an excellent indicator. Also, the indisputable advantages of this type of operation are the lack of age restrictions on the procedure and the wide mechanical capabilities of the implanted device, which practically do not differ from the physiological functions of the natural joint.
After the seventh or eighth week, when the muscle tissue and the joint capsule, which were also injured by surgery, are already cured, the exercises intensify, and in most cases the patient is freed to practice sexual activity and also to ride.
The patient needs to strengthen the muscles of the existing thigh, especially the gluteal muscles, since they greatly contribute to the stability of the “new joint” and for the patient to walk and carry out their activities without compensation. At this stage, exercises are already performed for all muscles of the lower limb. As the patient develops in strength and mobility, he is taught to wear shoes, dress and collect objects on the floor. The latter also performs balance training, motion control, and more intense activities in physical therapy, such as training on unstable surfaces such as a trampoline.

An example of bilateral hip arthroplasty with short-stem prostheses. Currently, it is used very rarely due to poor attachment of the implant leg to the bone.
The traditional set for a complete artificial analogue of the joint includes a leg with an elongated end, which will serve as the head, as well as a cup with an insert, which plays the role of articular cartilage.
The patient must spend at least 3-4 months in physiotherapy, and during this period he will be prepared to fulfill his daily and athletic life, if necessary. Arthroplastic surgery and a well-prepared rehabilitation process ensure that the patient returns to life as close to normal as possible, without compensation, which puts other joints at risk and without serious limitations.
What is postoperative care?
A patient suffering from arthroplasty of the hip joint must be careful about positioning and daily activities, as some movements of the hip joint, such as adduction, medial rotation and flexion above 90 °, may displace the prosthesis. Check basic precautions.
Surface replacement
In this case, during the operation, the final area of \u200b\u200bthe femur is replaced. As for the head and neck of the thigh, they remain unchanged.
This type of operation saves most of the joint, but despite this, surface prosthetics is considered very problematic.
This is called surface arthroplasty and it has one big minus - a metal friction pair, which gives the friction products and inflames the surrounding tissue.
This is justified by the fact that due to the metal implant installed in the joint, constant oxidation and friction will occur, which in turn will increase the risk of the inflammatory process in the surrounding tissues. That is why, in most cases, after superficial prosthetics, a person needs a second operation, which patients certainly do not want.

This is a cap implant "overgrown" with oxides due to the release of ions.
Single pole view
During such an operation, an implant is implanted that models only the head of the hip joint. It is introduced into it with the help of an elongated pin. In this case, the endoprosthesis head is constantly in contact with the cartilage structures.
It is possible to use this type of prosthetics only at the initial stages of the course of inflammatory and degenerative diseases, when not the entire joint is affected, but only its head. This will eliminate the affected part of the joint and at the same time conduct a minimum revision of the bone.
Bipolar technology
Many people believe that this type of operation is the exact opposite of a single-pole operation, but in fact this is an erroneous opinion, because these types of prosthetics are almost the same.
The significant difference between them lies only in the fact that bipolar prosthetic models have a movable head with two layers of shell, between which there is a special layer.

If you look closely, you can see two axes of movement of the components. The ceramic head moves in a polyethylene liner, which in turn also moves in the acetabulum component.
The duration of use of this type of prosthesis is about ten years.
Attention! If the patient needs his endoprosthesis to serve him as long as possible, then he is recommended to incline towards the choice of the total type. It is his design that can provide the most natural work of the prosthesis, which in function will be almost identical to a real joint.
In addition, hip replacement can be done using the following two techniques:
- Classic operation. This is the most commonly used type of procedure during which there is an open intervention with a large suture (usually the scar begins just above the end of the thigh and ends in its middle). This operating technique is convenient for a surgeon who fully sees the joint and has access to it.
- Mini invasive surgery. In turn, one can be anterolateral or posterolateral. The advantage of this operating technique is that during it the tissues are less affected, so the patient’s recovery process will be much faster.
Despite this, during such an operation, it is difficult for the surgeon to install a prosthesis, which requires additional time for anesthesia, as well as a high level of specialist skill.
It should be noted that with the classical technique of surgery, it is much easier to establish a good implant placement, because in this case the operational visibility will be greater. That is why surgeons claim that, despite the advantages of mini invasive methods, it is the classic open operation that is still more convenient and preferable.
Hip replacement disability
Some patients believe that after undergoing surgery for joint prosthetics, they are entitled to disability. In fact, for the official establishment of the group, the patient does not need the fact of the operation itself, but the consequences that the initial joint disease led to.
For example, disability is given after surgery, due to which a person can no longer move long distances without the help of crutches.

Also, quite often, patients ask themselves whether disability results from simultaneous replacement of two joints, because in this case the person’s motor activity will be significantly impaired, and the rehabilitation period will be even longer and more complicated.
Attention! When replacing two joints at the same time, the likelihood of a person having a disability is significantly higher, however, in order to really succeed, he should have all the documentary evidence, certificates and conclusions of the doctors about the intervention, recommendations and forced limitation (and sometimes complete loss) of physical activity. At the same time, the final decision on the establishment of disability is not made by the attending physician, but by a special commission.
Features of preparation for surgery
At the final decision on the operation two weeks before the operation, the person should conduct the following examinations:
- x-ray
- MRI of the joint;
- cardiogram;
- fluorography;
- hIV test
- hepatitis C test;
- general blood analysis;
- blood type analysis.
Also, without fail, a person should undergo an examination with the following specialists:
- Cardiologist.
- Dentist.
- Therapist.
- Surgeon.
- Infectionist.
- Orthopedist.

A positive attitude is a big plus for the success of the treatment.
In this gymnastics, the main load should be on the muscles of the hands, back and abs. Once again, it is impossible to strain a sore joint.
Remember! With heavy weight, the load on the endoprosthesis will be even greater, so both before and after the operation, you need to control your weight and prevent obesity. Moreover, it is precisely because of the extra pounds that doctors can refuse an operation until the moment when a person normalizes his weight.
A couple of weeks before the upcoming surgery, the patient must follow these tips:
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Go for proper nutrition. At the same time, it is most recommended to eat vegetables, fruits, nuts, homemade juices and low-fat sour-milk products. Moreover, greens, cereals and a decoction of dried fruits are very useful. This food should be aimed at strengthening human immunity.
- Discontinue treatment with those drugs that can affect the overall coagulation of blood. If a person cannot stop taking such drugs, he must inform the doctor who will perform the operation.
- Do not be nervous and not stressed, as this can contribute to an increase in heart rate, as well as increased blood pressure, which can lead to complications during or after surgery.

Two weeks before the operation, of course you can’t lose weight, but if you are overweight and you have surgery, then immediately lose weight. Excess weight complicates anesthesia, first verticalization, suture healing and implant wear.
Twelve hours before the procedure, a person needs to completely stop drinking water and food.
The general course of this operation is as follows:
- Tissue treatment with antiseptic and incision.
- Dissection of tissues for the appearance of the operational "field".
- The intersection of the femur and the creation of a special channel with an inverted tubular bone.
- The installation in the created hole of the wedge-shaped leg of the prosthesis, which should be as accurate as possible with the size of the bone.
- Pushing the spherical part of the implant onto the leg of the prosthesis.
- Placement of the cup in the insert and reduction of the entire implant.
- The installation of drainage in the wound and suturing.
- At the end of the procedure, the wound is treated with antiseptics and a bandage is applied on top. The patient goes to the ward.
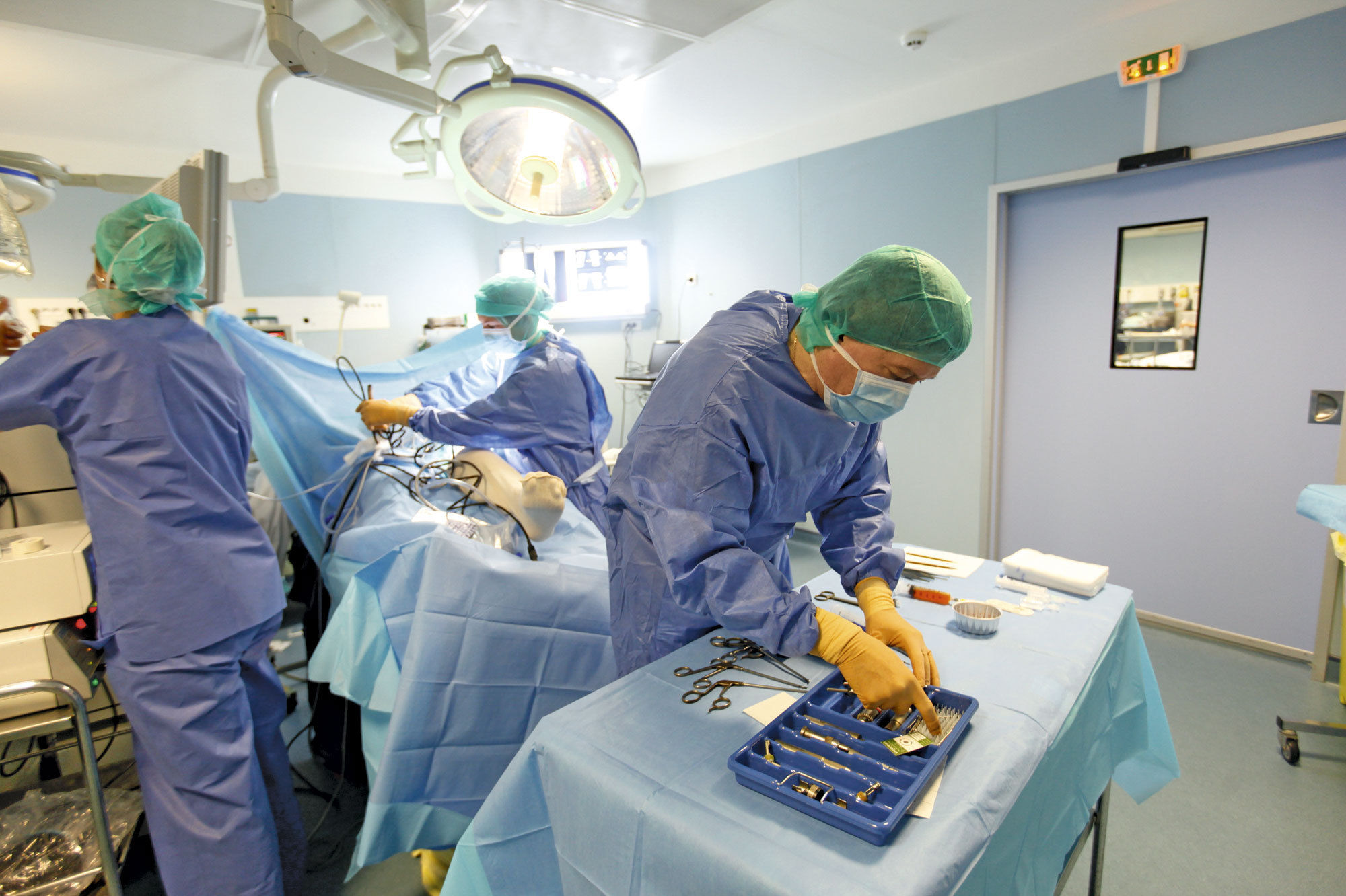
The patient is under anesthesia, tools are being prepared, the leg is in elastic knitwear.
Important! Replacement of both hip joints is recommended for younger patients, since it is much easier for them to immediately get to their feet after surgery, and they have more strength to move on crutches. Elderly patients after this intervention will need at least four days to get up and begin to walk slowly.
Complications
After replacing the hip joint, the patient may develop the following types of complications:
- Infection development. This happens if you operate under insufficiently sterile conditions. Symptoms of infection are pain, fever, and pus from the suture. This condition is treated with antiseptics and the introduction of antibiotics.
- Loss of sensation in the leg. This complication occurs with damage to nerve fibers.
- Common complications. They can be expressed as a heart attack, hypertension and poor discharge from anesthesia.
- Bleeding during surgery. It is possible with damage to the vessel.
- Thrombus. For its prevention, even before surgery, a person needs to enter antithrombolytic agents.
- The development of soft tissue necrosis. This happens with a violation of blood circulation and tissue nutrition, which leads to their death. Signs of this complication will be a loss of skin sensitivity, as well as its acquisition of a characteristic dark purple or black shade.
- Bone fracture. This complication happens when you fall, when the bone near the prosthesis is damaged.
- Joint dislocation. This complication most often occurs in the first days after surgery. To reduce the risk of dislocation, do not bend the leg strongly in the joint and move it to the side.
- Wear or loosening of the joint. It happens with prolonged use.
Even before the operation, patients ask the doctor about how much they will have to walk on crutches. In this case, doctors can not give a definite answer, because each case is individual and different techniques and types of prostheses are used in operations. Also, an important role in restoring a normal gait is played by the efforts that a person makes.
On average, patients have to use crutches for one month, after which they can be replaced with a cane. With a large volume of the prosthesis and total joint replacement, some patients need a longer time to restore physical activity without crutches.
Also, sometimes patients require repeated total replacement of the head of the hip joint in case of a fracture of the femoral neck. Indications for this are:
- infection;
- dislocation of the prosthesis;
- loosening of the prosthesis;
- inflammation.
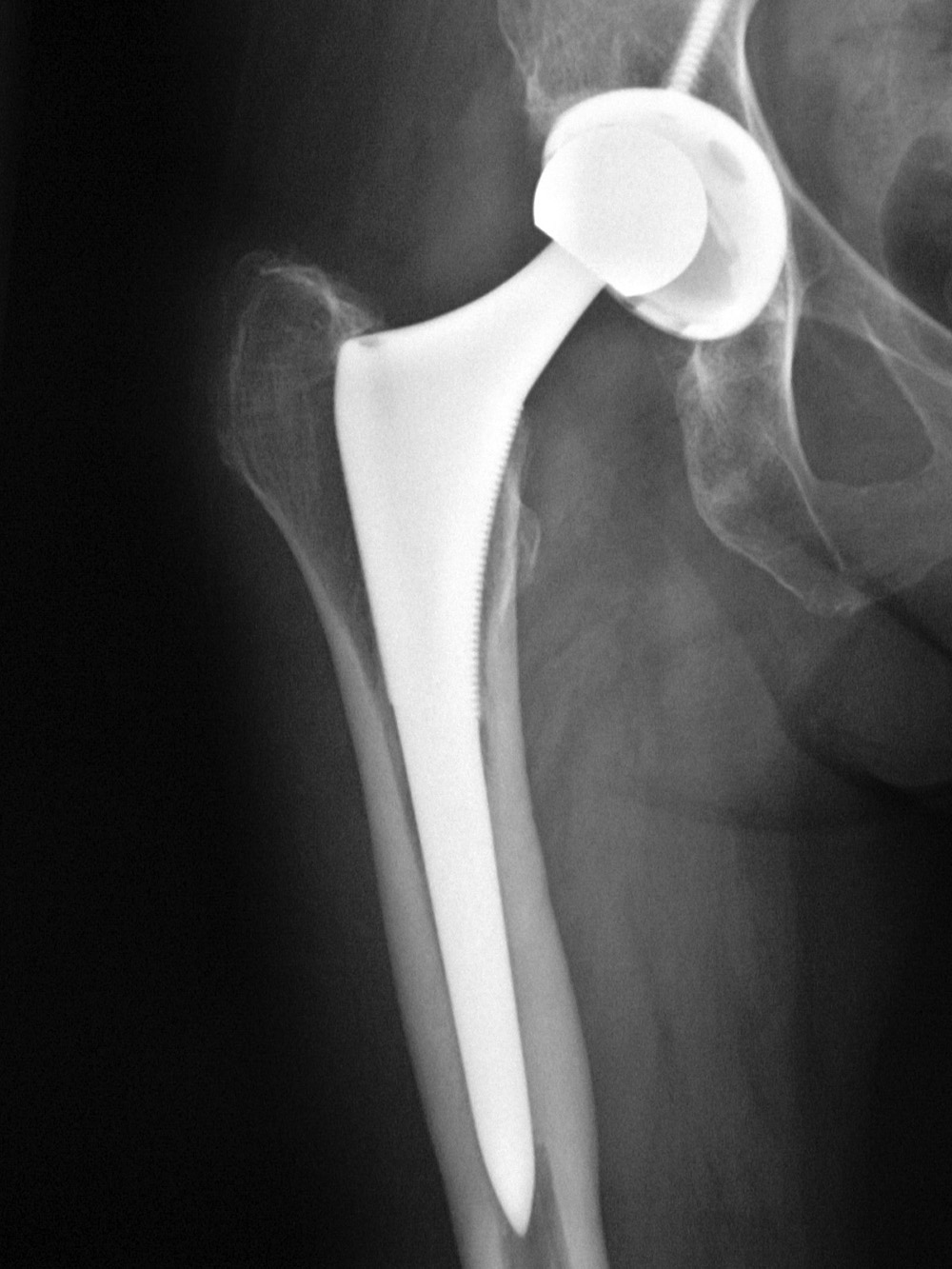
This rarely happens, but nevertheless you see how the liner of the acetabulum has thinned, due to which the endoprosthesis head has shifted higher. The foot, respectively, will also become shorter.

And this is a Dislocation, it happens due to a fall or a sharp incorrect movement.

So ceramic components can crack, but this happens very, very rarely.

So the implant can be destroyed if a person leads a very active lifestyle, and at the same time has a lot of excess weight.
Thanks to a wide selection of materials and manufacturers of joint analogues, it is difficult for patients to determine which prosthesis is better. Today, the following manufacturers are engaged in the development and manufacture of hip joints:
- Stryker.
- Biomet.
- Aesculap.
- Johnson & Johnson.
- Zimmer.
All these manufacturers produce high-quality endoprostheses that most naturally copy the natural joint of a person. It should be noted that all endoprostheses from such firms are of equal quality, so you cannot choose the best manufacturer from them.

Pay attention to the pink components, this is the same ceramics that wear out very slowly.
Moreover, the only company produces ceramic elements for such prostheses Ceramtech, which makes the difference between all endoprostheses even smaller.

In this case, the head of the femoral component is made of black ceramic under the trade name Oxinium. It is considered more perfect than usual.
As for the production technology, materials and size chart, the above-described leading companies have identical ones.
Not all patients can replace a hip joint, since this operation has the following contraindications:
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- recent stroke;
- severe heart disease;
- advanced form of renal or liver failure;
- HIV infection;
- oncological pathologies;
- bleeding disorder;
- necrosis of the femoral head or an active infection;
- the period of the course of viral diseases;
- active tuberculosis;
- advanced diabetes mellitus;
- serious mental illness;
- obesity 3 degrees;
- osteoporosis.
The following indications for the operation are distinguished:

Coxarthrosis clearly: on the left is a healthy surface of the femur, on the right is the last stage of coxarthrosis.
![]()
You see a very good and healthy seam. There are no scabs, the light is uniform, nothing oozes.
Important! In most cases, surgery is prescribed when other methods of treatment are simply not effective for a person. That is why it is simply unreasonable to consider any alternative that could replace this operation. Only a doctor can decide that a person needs prosthetics.
To extend the life of the prosthesis, you must follow these tips:
- Control your weight.
- Avoid physical overwork.
- Contact a doctor for any deterioration in the joint.
- Do not cross legs.
- Avoid excessive exercise.
- Practice gymnastics.
Implant Friction Pair
Current research and development scientists are aimed at increasing the period of use of endoprostheses, especially by patients of a young age. Because of this, the development of ever new elements and materials for artificial analogues of the joint.

Innovative developments pay great attention to friction pairs located in the zone between the cup and the prosthesis head. Thus, the most commonly used are the following friction pairs:
- metal + metal;
- ceramics + polyethylene;
- metal + polyethylene;
- ceramics + ceramics.
The selection of specific material for the prosthesis is carried out by a doctor. In this case, the specialist must take into account many factors, among which the main ones are the age and weight of the patient, his gender, the presence of concomitant diseases and the neglect of the main pathology.
The simplest and at the same time cheapest material for a prosthesis is a metal alloy (titanium, for example). These designs are quite simple and have good qualities of wear resistance. Such prostheses are recommended for the elderly.

Friction pairs from left to right: metal-polyethylene (cheap and short-lived), ceramic-polyethylene (middle ground), ceramic-ceramic (most durable and expensive)
Dentures made of polyethylene and ceramics are more expensive, but at the same time they have ideal properties for depreciation.
In terms of durability, as well as functions, the most optimal choice is a prosthesis made of ceramics and polyethylene. This combination provides very good glide and joint function. Moreover, such materials are hypoallergenic and provide long-term use.
Hip Replacement in Russia
Today, every citizen has the right to prosthetics for free under the quota. For this, a person needs to prepare the following documents:
- copy of the passport;
- referral from a doctor about the need for surgery;
- copy of the statement with the diagnosis;
- copies of research results;
- health insurance confirmation documents.
After discharge, the rehabilitation period begins. It provides for the following medical recommendations:
- Until the stitches are removed, dressings must be done daily (treat the wound with antiseptics, replace the sterile dressing with a new one).
- On the third or fourth day, you need to slowly get out of bed and with the help of crutches learn to move around. The load on the leg should be incomplete.
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor (analgesics, anticoagulants, antibiotics if necessary).
- Every day, rewind the operated leg with an elastic bandage to normalize blood circulation and eliminate edema.
- After discharging home and removing the stitches, it is allowed to increase the load on the leg and move around with a cane.
- In the late rehabilitation period (5-8 months after surgery), a person can practice physiotherapy.

Buy yourself an exercise bike and give it 15-20 minutes every day, this will tone your leg muscles and generally improve the condition of the body. The main advantage of a bicycle is the lack of shock loads.
The permitted types of sports load after such an operation are swimming, gymnastics and table tennis. It is strictly forbidden to run and jump after an operation. Weight lifting is also contraindicated.
Important! Those women who have a metal endoprosthesis installed have an increased risk of complications during pregnancy, since iron oxide can penetrate into the fetus in an increased amount.
Types of joint fixation
The following main methods for fixing endoprostheses are distinguished:
- Cementless method. This method is the most common. In this case, the prosthesis is fixed by introducing implant particles with a rough surface into the prepared bone tissue.

Soreness and stiffness of one or both hip joints (TBS) leads to impaired motor activity of the legs, which in turn significantly worsens the usual way of life. In addition to the inability to dance or play sports, in severe cases, patients with TBS pathology are not able to serve themselves even in everyday life. Constant and severe pain, limitation of leg / foot functionality often lead the patient to the operating table.
Hip replacement surgery is really a salvation for many people, leads to the restoration of leg / leg functionality and significantly improves the quality of life. The surgical treatment of TBS is only a short step on the road to restoring a familiar lifestyle and working capacity. Of great importance is the recovery after surgery, because it is from the correct and lengthy rehabilitation that the patient's continued comfortable existence depends.
Hip anatomy
The largest bone joint in the human body is the hip joint. It experiences tremendous stress throughout the life of a person, as it is a combination of the lower extremities and the pelvis.
Structures of which TBS is formed:
- femoral head - the upper end of the bone in the form of a ball;
- acetabulum - a depression or funnel in both pelvic bones in which the femoral heads are fixed;
- articular cartilage - lines the acetabulum from the inside and is represented by soft cartilaginous tissue with gel lubrication, it is necessary to facilitate and “soften” the movement of the femoral head in the joint;
- synovial fluid - liquid in the form of jelly, located in the joint cavity, which provides nutrition to the cartilage, and also softens the friction between the surfaces of the joint;
- ligaments and joint capsule - consist of dense connective tissue, designed to hold joint surfaces, ensure the stability of TBS and prevent its dislocation.
Movement in TBS is due to contractions of the muscles and tendons surrounding the joint. The similar structure of TBS makes the bone joint mobile and provides movement in almost any plane and direction. Such a range of movements adequately provides support, walking and the production of strength exercises.
Often, replacement of TBS is required after a serious injury. But often, indications for endoprosthetics are transferred diseases of bones and / or joints. Various degenerative processes in TBS cause pain and impair mobility, and in severe cases lead to the complete destruction of the femoral head and other components of the joint.
Endoprosthetics TBS
Endoprosthetics for TBS is a complex and lengthy surgical intervention, during which worn (destroyed) parts of the joint are replaced by artificial ones. The prosthesis, which replaces the "old" TBS, is called an endoprosthesis, as it is installed inside the (endo) body.
Who needs TBS endoprosthetics
Replacing TBS is advisable only in case of serious structural damage and impaired joint function, when walking and any physical activity causes pain and is almost impossible. In each case, the decision on the issue of endoscopic replacement surgery should take into account the capabilities of the operation, its necessity and benefit.
Indications:
- degenerative-dystrophic arthrosis of TBS (coxarthrosis) in the case of bilateral joint damage having a 2 - 3 degree;
- 3 degree of coxarthrosis of one TBS;
- coxarthrosis 2 - 3 degrees of one TBS, combined with ankylosis (complete immobility) of another TBS;
- ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritisleading to unilateral or bilateral ankylosis of TBS;
- aseptic necrosis, when the head of the bone is completely destroyed either due to circulatory disorders, or as a result of trauma, which is often found in young men and is not completely explainable;
- femoral neck fracture, as a rule, in elderly people, femoral head fractures (after a fall or injury);
- the formation of a false joint (in elderly patients);
- dysplasia of TBS, especially congenital;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders in the bones (osteoporosis or osteoarthritis);
- malignant neoplasms of the head or neck of the femur, both primary and metastases
- post-traumatic arthrosis;
- perthes disease - necrosis of the femoral head.
The main signs that signal the need to replace a hip joint include:
- a significant decrease in volume in TBS;
- stiffness of TBS;
- severe pain, even intolerable when moving;
- long-lasting pain syndrome.
Contraindications
Endoprosthetics of TBS can be performed not in all cases. Contraindications for joint replacement are divided into absolute (surgery cannot be done at all) and relative (with caution and under certain conditions).
Relative contraindications include:
- oncological diseases;
- chronic somatic pathology;
- liver failure;
- overweight (3 degree);
- hormonal osteopathy.
Absolute prohibition of surgery in case of:
- the impossibility of independent movement (replacement of the joint is impractical and only increases the risk of complications due to surgery);
- chronic cardiovascular pathology (heart failure and severe heart defects, arrhythmias), cerebrovascular accident and decompensated hepatic-renal failure (high risk of worsening condition);
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, which are accompanied by respiratory and ventilation failure (asthma, emphysema, bronchiectasis, pneumosclerosis);
- inflammatory processes in the field of TBS (damage to the skin, muscles or bones);
- the presence of foci of chronic infection that must be examined (carious teeth, tonsillitis, chronic sinusitis or otitis media);
- recently transferred sepsis (3 - 5 years before a possible intervention) - a high risk of suppuration of the endoprosthesis;
- multiple allergies, especially to a drug;
- paresis or paralysis of the leg to be operated on;
- severe osteoporosis and insufficient bone strength (high chances to break a leg in the thigh area even after a perfectly performed operation);
- the absence of a bone marrow canal in the hip bone;
- immaturity of the skeleton;
- acute diseases of the vessels of the legs (thrombophlebitis or thromboembolism).
Types of endoprostheses
An artificial joint, which is replaced by a pathological altered TBS, should have the following characteristics:
- sufficient strength;
- reliability of fixation;
- high functional abilities;
- inertness (biocompatibility) to body tissues.
The load on the artificial joint is greater than on its own due to the lack of cartilage and synovial fluid, which reduce the load and friction. Therefore, for the manufacture of endoprostheses, high-quality metal alloys, polymers (very durable plastic) and ceramics are used. Usually in one endoprosthesis all of these materials are combined, more often a combination of metal and plastic - combined artificial joints.
The most durable and resistant to wear are metal endoprostheses, their service life is 20 years, while the rest are no more than 15 years.
An artificial joint consists of:
- an endoprosthesis cup, which replaces the acetabulum of the pelvic bones, is made of ceramic or metal (but there is also plastic);
- the endoprosthesis head in the form of a spherical metal part with polymer spraying, which provides soft gliding of the endoprosthesis during leg movements;
- legs of the prosthesis, which accounts for the maximum load, therefore, is made only of metal (the leg of the endoprosthesis replaces the neck and upper third of the hip bone).
Endoprostheses by type of endoprosthetics TBS
The classification of artificial joints for arthroplasty of TBS includes their division into:
Single pole
They consist only of the legs and heads, which replace the corresponding parts of the hip bone, while the acetabulum remains its own "native". Such operations were often performed earlier, but due to poor functional results and a large number of destruction of the acetabulum, which leads to the failure of the prosthesis in the small pelvis today are rarely performed.
Bipolar
Such endoprostheses are called total and are used for total endoprosthetics of TBS. During the operation, not only the head and neck of the hip are replaced, but also the acetabulum (an endoprosthesis cup is installed). Bipolar endoprostheses are well fixed in the bone tissue, adapted as much as possible, which increases the success of the operation and reduces the number of complications. Such endoprostheses are suitable both for endoprosthetics of elderly patients with osteoporosis and for young active people.
Types of fixation of implants
The success of the operation is ensured not only by the correct choice of the endoprosthesis, but also by the method of its installation. The goal of hip joint arthroplasty is the most durable and reliable fixation of the implant to the bone to provide the patient with free movement in the leg after surgery.
Options for fixing prostheses:
Cement
For such an implant placement, a special biological glue is used, the so-called cement, which, after hardening, firmly fixes the endoprosthesis to bone tissues. Cement is prepared during the operation.
Cementless
This implant fixation is based on its special design. The surface of the endoprosthesis is equipped with many small protrusions, recesses and holes. After some time, the bone tissue grows through the holes and indentations, thus forming a single system with the implant.
Hybrid
Mixed implant placement combines cement and cementless mounting methods. This option involves screwing the endoprosthesis cup into the acetabulum and fixing the leg with cement.
The choice of fixation option for the endoprosthesis is determined by the anatomical features of the bone and the medullary canal, and, of course, the age of the patient. Both cement and cementless fixation have pros and cons:
- high temperature of surrounding tissues during cement hardening, which increases the risk of rejection of the implant or its failure in the pelvic cavity;
- on the other hand, with cement fixation, rehabilitation time is shortened, but the use of such fixation in elderly patients and in the presence of osteoporosis is limited;
- cementless fixation increases the rehabilitation period, but is preferable for young people, as they may require replacement of the endoprosthesis (re-endoprosthetics);
- hybrid fixation is the gold standard in endoprosthetics and is suitable for both young and elderly patients.
Preparation and progress of the operation
The decision on hip arthroplasty is made by the orthopedic surgeon together with the patient. In addition to the necessary diagnostic procedures (radiography, MRI and ultrasound of the operated area), the doctor examines the legs, reveals the features of the pathology and the degree of damage to the bone structures. During the examination, a suitable endoprosthesis for this patient is selected.
Additional studies and analyzes are also prescribed.
Before surgery
The patient is hospitalized one day - two before the appointed endoprosthetics date. In the hospital are appointed:
- UAC and OAM;
- blood glucose;
- blood chemistry;
- blood coagulation analysis (platelets, prothrombin, prothrombin index, bleeding and coagulation time);
- blood per group and rhesus;
- blood electrolytes;
- tests for HIV infection, syphilis and hepatitis;
- radiography of the lungs;
- determination of respiratory functions;
- according to the advice of other specialists.
The patient is informed about possible complications during and after the operation, they take written consent to the operation and instruct how to behave during and after the surgery.
Examination of the anesthesiologist includes the choice of anesthesia, preference is given to spinal anesthesia - an “injection in the back” (less harmful and optimal for elderly patients).
A light dinner is allowed on the eve of the operation. In the morning, the skin in the area of \u200b\u200bthe hip joint is thoroughly shaved, the legs are bandaged with elastic bandages or compression stockings are put on. In the morning, the patient is not allowed to drink and eat.
Operation progress
After transporting the patient to the operating room, anesthesia is performed and the surgical field is treated with antiseptics. The surgeon dissects the skin and muscles (up to 20 cm in length) and opens the intraarticular capsule and displays the femoral head into the wound. He then resects the hip bone, including the head and neck, and exposes the bone canal.
The bone is modeled according to the shape of the implant, which is fixed in the bone channel in the most appropriate way (usually with cement). Drill process the acetabulum and completely remove articular cartilage. An endoprosthesis cup is installed and fixed in the treated funnel.
The final stage of the operation is suturing of dissected tissues and installing drainage in the wound to drain the discharge. A bandage is applied.
The duration of the operation is 1.5 - 3.5 hours.
Possible complications
The issue of complications of hip replacement is often of interest to patients. Any surgical intervention carries the risk of failure. Endoprosthetics of TBS is a very complex and extensive operation, and even taking into account contraindications, correctly selected indications, following the rules and postoperative recommendations, adverse results are possible.
All the complications of this surgical treatment are divided into 3 groups:
- During surgery
This group includes the development of bleeding in the wound, an allergy to narcotic drugs or a violation of cardiac activity, less often thromboembolism and fracture of bone formations of the joint.
- In the early recovery period
Bleeding from a wound, suppuration of a wound or an implant, hematoma of the operated area, failure of the endoprosthesis with its rejection, osteomyelitis, anemia, or dislocation of the hip joint are possible.
- Remote
Similar complications develop after the patient is discharged from the hospital. These include dislocation of the endoprosthesis, the formation of rough scars in the postoperative region, which reduces mobility in the joint or loosening of parts of the joint prosthesis.
Talk about pricing
All patients, without exception, are interested in whether the operation is paid, and if so, what is the cost of arthroplasty. In Russia today it is possible to carry out surgical treatment of the hip joint according to the following programs:
- free of charge, if there is a compulsory medical insurance policy (as a rule, in this case there is a queue for 6 to 12 months);
- free of charge according to the quota of VMP (high-tech medical assistance) - certain circumstances are needed for which benefits are provided;
- paid in a public or private clinic.
When buying an artificial joint, one should not be based on price, but on the model, diagnosis and age of the patient. For example, an endoprosthesis for surgery for coxarthrosis will cost more than an implant needed for a fracture of the femoral neck. So the operation is very complex, the professionalism of the surgeon and the virtuosity of the execution are important, and not an expensive implant. In the case of a medical error, the development of negative results can be with the most high-quality and expensive endoprosthesis.
Only a doctor can choose the optimal implant model, therefore it is better to entrust the choice of endoprosthesis to the operating surgeon.
The most popular implant models are manufactured by international companies such as DePuy and Zimmer.
When choosing an endoprosthesis, the material from which the components of the implant are made should be taken into account:
- metal / metal - this combination is resistant to wear, service life is 20 years or more, ideal for men with an active lifestyle, but not recommended for women who are planning a pregnancy (high risk of metal ions entering the fetus); the price is quite high and toxic products may form on the surfaces of the endoprosthesis during friction, therefore they are rarely used;
- metal / plastic - an inexpensive implant, the toxicity of friction products is moderate, but short-lived design (no more than 15 years); suitable for people with an unsportsmanlike character, leading a calm lifestyle and accessible to senior citizens;
- ceramic / ceramic - good for any age and gender, they are durable and non-toxic, but expensive (as a disadvantage - they can creak when moving);
- ceramic / plastic - differ in cheapness, quick wear and short-lived, optimal for older men and women.
The price for endoprosthetics is the sum of the cost of the implant, the cost of the operation plus hospital stay. For example, the minimum price for a DePuy implant is $ 400, and for a Zimmer $ 200. The average cost of surgical treatment ranges from 170,000 to 250,000 rubles, and together with a hospital stay up to 350,000. In total, the financial costs of treatment will be about 400,000 rubles.
Rehabilitation and life with a prosthesis
Rehabilitation after hip replacement is an important and lengthy process that requires great patience and perseverance from the patient. It depends on the patient how the leg will move in the future and whether it will return to the usual way of life.
After hip joint arthroplasty, all the measures taken are aimed at restoring motor activity in the operated joint and should begin immediately (after departing from anesthesia) after surgery. Rehabilitation includes:
- early activation of the patient, all measures should be performed continuously, sequentially and in combination;
- physiotherapy exercises;
- breathing exercises;
- massotherapy;
- intake of vitamins and minerals that strengthen bones and joints;
- balanced diet;
- limitation physical activity and sports activities.
There are 3 recovery periods:
- early postoperative, which lasts up to 14 - 15 days;
- late postoperative, lasts up to 3 months;
- remote - from 3 to 6 - 12 months.
Operation: first day
The first day of the postoperative period, the patient is in the ICU (intensive care unit), where they monitor vital signs and prevent the development of possible complications. After the operation, antibiotics and coagulants are prescribed, and the legs must be bandaged with elastic bandages (prevention of stagnation of blood). The dressing is changed and the urinary catheter is removed the next day. The patient should begin the first exercises after surgery immediately after leaving anesthesia:
- movement of the toes - to bend and unbend;
- to bend and unbend the foot in the ankle back and forth (about 6 sets per hour in a few minutes, until the foot is slightly tired);
- foot rotation of the operated leg 5 times in one direction (clockwise) and 5 times in the other;
- movements with a healthy leg and hands without restriction;
- slight bending at the knee with the operated leg (smooth sliding of the foot over the sheet);
- alternating tension of the left and right buttock muscles;
- alternately lifting one or another straightened leg 10 times;
All exercises in the first day and later must be combined with breathing exercises (prevention of stagnation in the lungs). When muscle tension should be inhaled deeply, and when relaxing, exhale slowly.
Sitting and walking on the first day is prohibited. Also, you can not lay on your side, you can only half-sided with a pillow between the legs.
While the patient is in a horizontal position, especially in people with somatic diseases of the heart, bronchopulmonary system, he is prevented from the formation of pressure sores (changing the position of the body, massage the skin over the bony protrusions and back, regularly changing clothes, treating with camphor to alcohol).
Second - tenth day
On the second day, the patient is transferred to a common room and the motor regime expands. You can try to sit down in bed already 2 days after the operation, preferably with the help of medical staff. When you try to sit down, you need to help yourself with your hands, and then lower your legs from the bed. It is important to sit, leaning back, placing a roller behind the back. You should also remember the main rule: the bending angle in the hip joint should not exceed 90 degrees, that is, the TBS should not be overbent, which is fraught with dislocation of the implant or damage to its components. To comply with this rule, you just need to make sure that the TBS is above the knee.
Doctors are allowed to take the first steps on the second or third day. The patient should be prepared for pain that occurs in the first days after arthroplasty. The first steps are also being carried out with the support of medical staff. The patient should be provided with a special frame (walkers) or crutches. Walking without crutches is possible only after one and a half to 3 months after the operation.
When moving to a standing position, certain rules must be observed:
- first, the operated limb hangs down with the help of hands and a healthy leg;
- leaning on a healthy leg with crutches, try to stand up;
- the operated leg should be suspended, any attempt to lean on it with all its weight for a month is prohibited.
If the recovery period is satisfactory, then after a month it is allowed to use a cane instead of crutches as a means of support. It is strictly forbidden to rely on a sore leg for the first month after surgery.
- alternately bend at the knee and lift one or the other leg - an imitation of walking in place, but with support on the back of the bed;
- standing on a healthy leg, take aside and restore the operated limb to its initial position;
- standing on a healthy leg, slowly and smoothly take the sore leg back (do not overdo it) - extension of the hip joint.
It is allowed to roll over in bed on the stomach from 5 to 8 days, and the legs should be slightly divorced with the help of a pillow between the thighs.
The intensity of the loads and the expansion of the range of motion should increase gradually. The transition from one type of exercise to another should not be done before 5 days.
As soon as the patient begins to confidently get out of bed, sits down and walks on crutches for more than 15 minutes three times a day, they start training on an exercise bike (10 minutes once or twice a day) and begin to learn to walk upstairs.
When lifting, first a healthy leg is put on the step, then the operated one is carefully substituted for it. During the descent, crutches are transferred to the lower step, then the operated limb, and then healthy.
Remote rehabilitation period
The final stage of recovery begins 3 months after arthroplasty. It lasts up to six months or more.
A set of exercises to perform at home:
- lie on your back, bending and pulling the right and left leg to the stomach in turn, as when riding a bicycle;
- lie on a healthy side (a pillow between the hips), raise the operated straight leg, maintain position as long as possible;
- lie on your stomach and bend - to extend the limbs at the knees;
- lie on your stomach, raise your straight leg and take it back, then lower it, repeat with the other limb;
- perform half-squats from a standing position, leaning on the back of a chair / bed;
- lying on your back alternately bend your knees, without taking your feet off the floor;
- lying on your back, alternately take one and the other leg to the side, sliding on the floor;
- lay the pillow under the knees and alternately unbend the legs in the knee joints;
- standing, leaning on the back of the chair, raise the operated leg forward, then take it to the side, then back.
Apartment preparation
In order to avoid possible difficulties after discharge of the patient from the hospital, you should prepare the apartment:
Remove all carpets to prevent feet or crutches from clinging to them.
- Walls
Place special handrails in high-risk areas: in the bathroom and toilet, in the kitchen, next to the bed.
- Bed
If possible, get a medical bed, from which you can change the height. It is not only comfortable to relax on, but also easier to sit down and get out of bed.
- Bathroom
It is advisable to wash in the bathtub or take a shower while sitting, either by putting a special board on the edges of the bathtub, or by putting a chair with non-slip legs in the shower stall. To fix the handrail on the wall by the bathtub to facilitate the process of rising and squatting in the bathtub.
- Restroom
The patient should remember the rule - the bending angle in the TBS should not exceed 90 degrees. But the standard height of the toilet does not allow this rule to be observed, so either an rubber ring or a special nozzle is placed on the toilet. Handrails are also installed on the walls next to the toilet to facilitate squatting and standing up.
What is allowed and what is prohibited
After the operation, no matter how long it was carried out, it is strictly forbidden:
- sit on a low surface (chairs, armchairs, toilet bowl);
- cross legs while lying on your side or on your back;
- sharp turns of the body with fixed legs and pelvis (back or sideways), you should first rearrange the legs in the right direction;
- lie on your side without a roller between the knees;
- sit cross-legged or cross limbs;
- sit for more than 40 minutes.
It is possible after arthroplasty:
- rest in a horizontal position on the back up to 4 times a day;
- dress only sitting, put on stockings, socks and shoes with the help of loved ones;
- when sitting, spread the feet to a distance of 20 cm;
- to do simple household chores: cooking, dusting, washing dishes;
- walk independently (without support) after 4 - 6 months.
Question answer
Question:
How to eat after surgery?
Due to the fact that the patient has reduced motor activity after implant placement, it is necessary to monitor the caloric intake to prevent weight gain, which slows down the patient’s recovery. Fatty and fried foods, pastries and pastries, marinades, smoked meats and seasonings should be discarded. It is necessary to expand the diet with fresh and baked fruits and vegetables Low-fat varieties of meat (beef, veal, chicken) and fish. Strict ban on alcohol, strong tea and coffee.
Question:
When are they discharged home?
If the postoperative period was uneventful, then discharge from the hospital is carried out on 10-14 days, immediately after removal of the sutures.
Question:
When is drainage removed from the wound?
Drainage is removed after cessation of discharge of the discharge, as a rule, this occurs on 2 - 3 days.
Question:
I began to worry about pain after surgery (a year has passed). What is the reason for this?
It is necessary to undergo an examination with the operating doctor and make sure that everything is in order with the endoprosthesis. If there are no complications, you should consult a neurologist, perhaps the pain is associated with lumbar osteochondrosis.
Question:
Is arthroplasty possible at any age?
Not. Doctors do not recommend surgery for people under 45 years of age. Firstly, this is due to the limited use of the implant (maxim up to 25 years), and secondly, in young patients, the endoprosthesis wears out faster due to physical activity.
Question:
Is an operation possible with simultaneous replacement of both hip joints?
Yes, it is possible, but it is produced extremely rarely and for health reasons (more often after an injury). Double endoprosthetics increases the likelihood of developing postoperative complications and complicates the course of the recovery period.
Question:
I had TBS endoprosthetics. When do i need x-rays of the operated joint?
X-ray examination is carried out 3 months after implantation of the endoprosthesis in order to determine the state of fixation of the implant and bone structures.